Table of contents
- 1 What is Blockchain Technology? A Comprehensive Guide
What is Blockchain Technology? A Comprehensive Guide
One of the most transformative and disruptive innovations of the rapidly evolving digital landscape is blockchain technology. Though it gained notoriety as the underlying technology powering cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, its potential reaches well beyond digital currency. What is blockchain? In this Ultimate Guide, we break down what blockchain technology is in-depth: what blockchain technology is, its use cases, and how you can use blockchain technology.
Key Takeaway: Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across many computers. It ensures security and transparency by cryptographically linking blocks of data, making it nearly impossible to alter past records.
The Origins of Blockchain
Therefore, knowing where it comes from can help you comprehend what blockchain technology is really capable of doing. Although Bitcoin opened the world’s eyes to blockchain in 2009, the theoretical principles behind the technology date back much further. In 1991, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta proposed a cryptographically secure chain of blocks in which document timestamps could not be backdated—the blocks were linked by cryptography. This vision formed the basis for what we now refer to as the blockchain.

But it was the soon-to-be pseudonymous entity named Satoshi Nakamoto who released the Bitcoin whitepaper in 2008, introducing the initial proposal for a “purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash.” The design combined multiple ideas from the field of cryptography, resulting in a decentralized, secure, and transparent ledger—the Bitcoin blockchain.
Understanding the Mechanics of Blockchain
After all, at its essence, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records activity on multiple computers. It is imperative to have decentralization. Different from conventional databases, which are controlled by a single organization, blockchain distributes control to participants, which increases its security and openness.
Key Components of a Blockchain Block
Blocks
A blockchain consists of blocks. Each block contains a timestamp, a list of events, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. These hash links form the “chain,” and changing one block would require changing all the blocks that follow.
Nodes
Nodes are computers or people who participate in the blockchain network. They store a copy of the blockchain and verify that transfers are authentic. Any one of us can be a node in a public system like Bitcoin. In private or permissioned blockchains, nodes are already invoked.
Consensus Mechanisms
These are the rules that ensure consensus on the current state of the blockchain across all nodes. Some common methods are:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Bitcoin requires nodes (miners) to solve difficult cryptographic puzzles in order to validate transactions and create new blocks. What is known as Proof of Work (PoW). It consumes a lot of energy but is safe.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): A more eco-friendly alternative that allows nodes (validators) to stake cryptocurrency in order to assist in verifying transactions. The more stake somebody has, the more probable they will get. Ethereum is transitioning to Proof of Stake.
- Other Mechanisms: This can include any mechanism that is not a POW or POS, for example, Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Proof of Authority (PoA), etc. Each has its features that make it more suitable for multiple blockchain needs.
Hashing with cryptography
Hashing is one of the major protectors of blockchain. You digest inputs (transaction info here) into a string of fixed length. Making small alterations to the data results in a very different hash. This ensures the integrity of the data; any effort to tamper with it is quickly identified.
How the Transaction Works
- A transaction is initiated and signed with the initiator’s private key.
- Then it is broadcast to all the nodes in the network.
- In the consensus approach, the nodes verify that the transaction is legitimate.
- All deals that are checked out are added to a new block.
- This new block is cryptographically connected to the previous block, forming an immutable chain.
Types of Blockchains
Blockchain is not one thing—there are different layers and approaches to reach them. If you want to understand what blockchain technology is all about, you’ve got to know about these differences.
Public Blockchains
Because these do not require approval, anyone can participate in the network, assist in verifying transactions, and store a copy of the blockchain. Use cases such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are excellent! Public blockchains are geared towards transparency and censorship resistance.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are permissioned, meaning a single entity controls who can access the network and what users can do. Most of its use is for internal business purposes of businesses. They are less decentralized but give you more privacy and control over them. Other examples include Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda.
Consortium or Federated Blockchains
Both these things are at once public and private. They are regulated by multiple entities, allowing them to be conducive for cross-organizational collaboration. One example is Ripple (XRP), which is an example of a cooperative blockchain and is used in the money business.

Hybrid Blockchains
Hybrid is a flexible blockchain since it incorporates elements of public and private blockchains. They give you the ability to determine who may join and what information may be viewable to all. Dragonchain is an example of a mixed blockchain platform.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
There are so many advantages of using blockchain technology that it has the potential to revolutionize everything.
Decentralization
By distributing power throughout a network, blockchain eliminates single points of collapse and lessens the threat that one group would censor or alter the information. According to a Deloitte 2023 study, 82% of people employed in the financial services sector feel that blockchain technology is versatile, and it is likely to be used broadly.
Transparency and Immutability
All confirmed transactions are recorded in a permanent public log (in public blockchains). This creates trustworthiness and responsibility in people.
Enhanced Security
Because it utilizes cryptographic hashing and decentralized consensus processes, blockchain is incredibly secure and relies on a decentralized network to make hacking and tampering very difficult. For example, the Bitcoin blockchain has never been successfully attacked since its inception. “Bitcoin has been one of the best performing assets for the last 10 years, going up over 9,000,000%.” (Bloomberg)
Efficiency and Speed
Blockchain technology can hugely simplify processes by eliminating middlemen and automating transactions via self-executing agreements (known as smart contracts) that are coded directly into software.
Savings on costs
A substantial amount of expenditure can be reduced with blockchain owing to the reduced reliance on middlemen and the automation of roles and processes. By making things more efficient through the tech, the World Economic Forum is saying blockchain could save the shipping industry $5.7 billion annually. (Source: WEF)
Possible Uses for Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is commonly associated with cryptocurrencies; however, its application is manifold and revolutionizes processes and makes new opportunities in varied fields.
Financial Services
- Cryptocurrencies: Blockchain is used by cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others to make transfers secure and decentralized. You can also read about the best crypto exchanges and apps
- Cross-border Payments: Blockchain can significantly expedite and reduce the cost of cross-border money transfers.
- Digital Identity: Safe and verifiable digital identities should be available to speed up Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures.
- Trading and Settlement: Blockchain can accelerate trading and reduce settlement rates.
Managing the supply chain
Blockchain makes supply lines more visible and traceable, so all parties involved in a supply chain can see where goods come from and where they end up inside stores. Walmart, for instance, is developing a way to use blockchain to track where food comes from, which enhances food safety and cuts the time it takes to respond to food recalls.
Healthcare
- Patient Records: Storing and handling the patient data securely is the prime part of the healthcare industry, and with the help of blockchain, patients can get control of their data while providers can easily share data.
- Drug Supply Chain: Using a blockchain to keep track of drug transactions can prevent fake pills and ensure the reliability of the drug supply chain.
- Clinical Trials: By creating a more transparent, tamper-proof log of clinical study data, blockchain can streamline the process.
How Voting Works
Voting systems based on the blockchain can make elections safer, more transparent, and more verifiable. There are pilot projects underway in some countries, but they are still only tests.
Intellectual Property
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize copyright ownership and management by creating immutable records of creation and ownership, which facilitate license transactions and enable users to track royalties.
Real Estate
By establishing the property records and being accessible and secure, blockchain helps to expedite property transactions, reduce fraud, and help streamline the land registry.
Government
Governments are exploring blockchain for various reasons, including:
- Digital Identity: As an example, blockchain is used in Estonia’s e-Residency system to maintain security for digital identities.
- Taxation: Make it easier to pay taxes and more transparent about it.
- Public Procurement: more open, less corrupt government procurement systems.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain
Despite the potential of the blockchain technology, it also suffers from some limitations and challenges.
Scalability
Scalability still poses a significant challenge, especially for public blockchains like Bitcoin. As the volume of transactions rises, the network could become congested, leading to longer processing times and higher fees. Solutions Pieter Wuille is definitely going to be working on are sharding, off-chain transactions, alternative consensus techniques, etc.
Energy Utilization
While blockchains based on proof-of-work (like Bitcoin) have high energy usage, raising environmental concerns. According to the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index, Bitcoin mining uses more energy per year than in countries like Argentina. Source: CCAF
Regulation
The legislative framework for blockchain and crypto is still evolving and substantially different across jurisdictions. This uncertainty can stifle adoption and innovation.
Interoperability
Most blockchains work in silos, with no interoperability. This curtails the seamless transfer of data and assets between different blockchain networks. Projects like Polkadot and Cosmos aim to solve this problem by building compatible ecosystems of blockchains.
Security Vulnerabilities
While the core blockchain technology is incredibly secure, smart contracts or application layers may have vulnerabilities. The risk was underscored by the 2016 DAO breach, which stole millions of dollars worth of Ether by taking advantage of a vulnerability in a smart contract. (Source: Gemini)
User Experience
Interfaces and applications within the blockchain can be complex and difficult for non-technical users to use. Easier to use means easier to adopt.
Threat of Quantum Computing
Powerful quantum computers and their theoretical advances may finally break the cryptographic systems behind blockchain security. Researchers are developing cryptographic schemes immune to attacks from quantum computers.
The Future of Blockchain
Despite these challenges, the outlook for blockchain technology appears bright. Current research and development efforts are addressing its limitations and uncovering new possibilities. The global size of the blockchain market as of the third quarter of 2023 was estimated to be $10.45 billion. It is expected to exceed $115.56 billion by 2028 (Source: Grand View Research, Inc.).
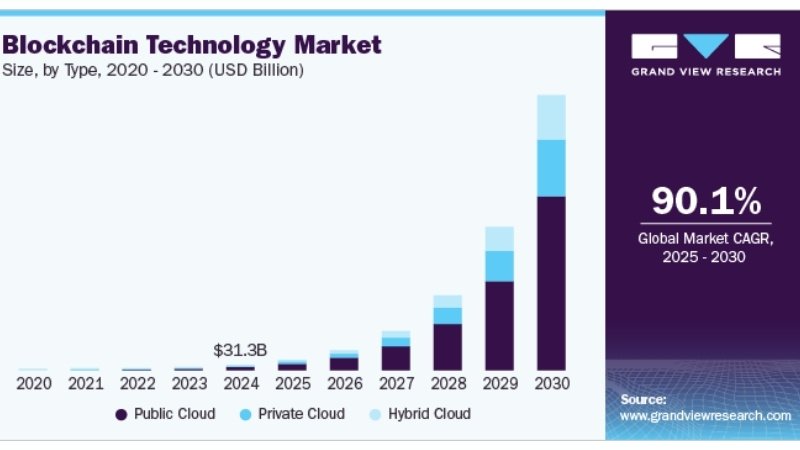
Emerging Trends
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Using blockchain technology to provide decentralized lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services, DeFi is growing rapidly and challenging traditional finance.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
NFTs came into prominence, allowing for unique ownership of digital assets, including art, collectibles, gaming, and more. Further research can be done about NFT Staking and NFT floor price.
Web3
Web3 refers to a decentralized version of the internet that is built on top of blockchain technology, offering individuals greater control over their data and online actions.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
So, you’re basically a central bank whose currency—which is a certain kind of currency—is under scrutiny, or CBDCs are being explored, and a lot of central banks are testing or doing pilot projects or simulations or plans.
Enterprise Blockchain Adoption
More and more businesses are using blockchain solutions, mainly in the fields of supply chain management, finance, and identity verification. According to a 2023 report by Gartner, the market for blockchain platforms will have a total market size of $20 billion by 2026.
Eco-Friendly Blockchain & Sustainable Solutions
As a response to the consumption of energy, the industry has moved towards sustainable blockchain technologies like Proof of Stake (PoS) and energy-efficient layer-2 alternatives.
The Road Ahead
Cryptocurrency technology has a long way to go. Its revolutionary potential is expected to grow exponentially as trends are observed converging with other technologies like AI, IoT, and big data. We expect to see in the next 10 years:
- Mainstream acceptance at an empowered level across industries
- Improved regulatory clarity and consistency.
- Better UI-friendly blockchain applications
- The same goes for new consensus processes and scalability solutions.
- Rise of DAOs and other novel governance structures
Key Takeaways
- Blockchain: It is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that enhances security and transparency.
- It includes blocks, nodes, and consensus mechanisms that ensure data integrity and network consensus.
- The key benefits include increased decentralization, transparency, greater security, and overall efficiency.
- Blockchain has multiple applications in finance, supply chain management, health care, and other industries.
- From scalability to energy consumption, from regulation to interoperability, all are roadblocks that people are actively solving through the process of innovation.
Conclusion
The Ins and Outs of Blockchain Technology It is more than just the building blocks of cryptocurrencies; it is a transformative force reshaping industries, empowering people, and redefining trust in the digital age. While there are still limits to the technology, its continuous innovation and expanding use suggest a bright future for blockchain. Within this progressive space, understanding the upsides and downsides of blockchain tech is vital for anyone looking to build a career or succeed in the future of the digital world.
Have you learned from this extensive introduction covering all the aspects of how exactly blockchain works, its history, and its future? Armed with this knowledge, you are now ready to navigate the ever-evolving world of blockchain and its profound implications for the future.
FAQ
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that allows for the secure and transparent recording of transactions. It eliminates the need for intermediaries and increases trust in financial and data-sharing ecosystems.
How does blockchain technology work?
Blockchain works by maintaining data regarding transactions in hash-linked blocks. Each block contains a timestamp, a hash of the previous block, and transaction data, allowing for security, transparency, and immutability in the decentralized network.
What are the main types of blockchains?
There is a wide variety of different types of blockchain networks: public (Bitcoin, Ethereum), private (Hyperledger, R3 Corda), consortium (Ripple), hybrid (enterprise-use cases), etc.
What are the benefits of blockchain technology?
Blockchain provides a host of benefits, including decentralization, transparency, increased security, reduced fraud, improved efficiency, and lower costs. It has a lot of applications in finance, healthcare, supply chain management, and digital identity systems.
What is the future of blockchain technology?
Eventual blockchain improvement entails rising adoption in decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, Web3, and enterprise purposes. Scalability, sustainability, and legal frameworks are shaping its role in the digital economy.













Pingback: Understanding Cryptocurrency Regulations and Their Importance
Pingback: What Does Crypto Mining Mean and How Does it Work?
Pingback: What is a Crypto Stock and How Does it Work? CoinFxPro
Pingback: What Does Decentralized Mean in Crypto? A Beginner's Guide? CoinFxPro