Table of contents
- 1 What is Bitcoin? A Deep Dive into the World’s First Cryptocurrency
- 1.1 Introduction to Bitcoin
- 1.2 How Does Bitcoin Work?
- 1.3 Bitcoin Wallets: Your Gateway to the Bitcoin Network
- 1.4 Bitcoin Price History: A Rollercoaster Ride
- 1.5 Is Bitcoin a Good Investment?
- 1.6 What is Bitcoin Halving?
- 1.7 Bitcoin vs Traditional Currency
- 1.8 Bitcoin Transactions in Detail
- 1.9 Bitcoin Security and Safety
- 1.10 Benefits of Bitcoin
- 1.11 What is Bitcoin Used For?
- 1.12 Bitcoin For Beginners
- 1.13 Conclusion: The Future of Bitcoin
- 1.14 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Bitcoin? A Deep Dive into the World’s First Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin has revolutionized the financial landscape, emerging as a groundbreaking digital currency that operates independently of traditional banking systems. But what exactly is Bitcoin, and how does it work? This comprehensive guide will explore every facet of Bitcoin, from its underlying technology to its potential as an investment and its impact on the world.
Introduction to Bitcoin
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin (BTC) is a decentralized digital currency, also known as a cryptocurrency, that uses cryptography for secure financial transactions and to control the creation of new units. It was created in 2008 by an anonymous individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto, and launched in 2009. Bitcoin was designed as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, allowing users to send and receive money directly without needing intermediaries like banks. Unlike traditional currencies that are issued by central banks, Bitcoin is not controlled by any single entity. According to a report by Cambridge University, as of 2024, there are an estimated 100 million active Bitcoin users worldwide, underscoring its growing adoption.
Key Features of Bitcoin
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning no single entity controls the system. This contrasts sharply with traditional financial systems controlled by central banks.
- Limited Supply: There will only ever be 21 million bitcoins, making it a scarce digital asset. This scarcity is a key factor in its value proposition, often compared to precious metals like gold.
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Transactions occur directly between users, without the need for intermediaries. This reduces costs and speeds up transaction times compared to traditional banking.
- Transparency: All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger, the blockchain, which allows anyone to verify their validity. This transparency enhances security and trust in the system.
- Security: Cryptography secures Bitcoin transactions, preventing counterfeiting and tampering. The use of cryptographic hash functions and digital signatures makes Bitcoin transactions virtually tamper-proof.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin transactions are transfers of value between Bitcoin wallets recorded on the blockchain. When a user wants to send Bitcoin, they create a transaction that includes the recipient’s address and the amount of Bitcoin they wish to send. The transaction is then signed with the sender’s private key, verifying that the user has control over the Bitcoin they are sending. This process is all done using a Bitcoin wallet and is generally very simple. In 2023, approximately 250,000 Bitcoin transactions were processed daily, showcasing the network’s robust activity.
Once created, the transaction is broadcasted to the Bitcoin network. This then goes to a mempool, where the transaction is considered “pending”. Bitcoin does not have accounts like traditional banks. Instead, bitcoin is associated with an address, which is controlled by the owner of that bitcoin. These pieces of bitcoin are called Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs).
Bitcoin Mining Explained Bitcoin mining is the process through which new Bitcoins are created and transactions are added to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computer hardware to solve complex mathematical problems. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoin and transaction fees. This process is known as the “Proof-of-Work” consensus mechanism, which requires computational work to validate transactions and secure the network. This method helps ensure the integrity of the blockchain. The energy consumption of Bitcoin mining has been a topic of debate. According to a recent study by the University of Cambridge, Bitcoin mining consumed around 110 terawatt-hours of electricity in 2023, a figure that continues to evolve as mining technology improves.
What is Bitcoin Blockchain? The Bitcoin blockchain is a public, distributed ledger that contains the entire history of Bitcoin transactions. It is structured as an ordered list of blocks, where each block contains a hash of the previous block, creating a chronological chain. Because the blockchain is distributed across a peer-to-peer network, every participant has a copy, which makes it difficult to alter or tamper with. The blockchain is transparent as all blocks and transactions are publicly available for viewing on a blockchain explorer. The blockchain is what allows Bitcoin to operate without a central authority. As of January 2025, the Bitcoin blockchain contains over 850,000 blocks, each containing numerous transactions.
Bitcoin Wallets: Your Gateway to the Bitcoin Network
A Bitcoin wallet is essential for managing your Bitcoin holdings. It stores your private keys, which are needed to authorize transactions. There are several types of Bitcoin wallets:
Bitcoin Wallet Types
- Hot Wallets: These wallets are connected to the internet and are convenient for everyday use. Examples include mobile wallets, desktop wallets, and web wallets. They’re easier to use but are also more susceptible to security breaches. A survey by the Blockchain Security Institute found that 60% of cryptocurrency losses occur through compromised hot wallets.
- Cold Wallets: Also known as hardware wallets, these wallets are stored offline, providing maximum security. They are ideal for long-term storage of larger Bitcoin holdings. Examples include USB devices designed for storing crypto. Hardware wallets account for a small percentage of total wallets, but hold a disproportionately large amount of Bitcoin, due to the high security they provide.
- Paper Wallets: These wallets involve printing your private and public keys on a piece of paper, which you then store securely offline. While offering a high degree of security, they are more difficult to manage.
How to Store Bitcoin Securely
It’s essential to store your Bitcoins safely and securely. Here are some tips:
- Use strong passwords: Protect your wallets with strong, unique passwords. Avoid using easily guessable information.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security to your wallet. 2FA can prevent unauthorized access to your wallet even if your password is compromised.
- Keep software updated: Make sure your wallet software is always up to date to protect from vulnerabilities. Regular updates contain security patches that can protect against known exploits.
- Backup your wallet: Regularly back up your wallet to prevent losing access to your Bitcoins. Backup should be stored offline, in a safe location.
- Consider a hardware wallet: For large amounts of Bitcoin, a hardware wallet provides enhanced protection. These devices store your private keys offline, making them very secure.
- Be wary of phishing attacks: Avoid clicking on suspicious links and double-check the authenticity of web pages. Phishing scams are a common way for hackers to steal Bitcoin.
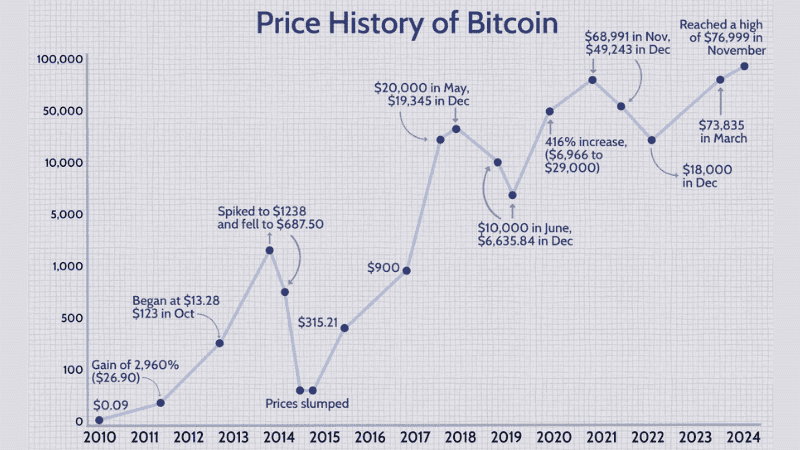
Bitcoin Price History: A Rollercoaster Ride
Bitcoin’s price has seen significant volatility since its inception. Its value has been known to experience significant rises and falls. While this may be alarming for some, many investors like it because they see the possibility for high returns, despite the risk. The price history of Bitcoin is a perfect example of risk and reward, with the potential to make significant returns, but also the potential to lose money.
Key Moments in Bitcoin Price History
Early Days (2009-2011): Bitcoin was initially valued at a fraction of a penny and then surpassed $1 in 2011. During this period, Bitcoin was primarily a niche technology with limited real-world use.
2013 Bull Run: The price experienced a significant surge, reaching over $1,000 before a subsequent crash. This bull run was driven by increased media coverage and speculation about the future of Bitcoin.
2017 All-Time High: Bitcoin’s price soared to nearly $20,000, attracting widespread media attention and new investors. The influx of new users led to increased demand and dramatic price appreciation.
Subsequent Bear Market (2018): Following the 2017 peak, Bitcoin’s price corrected significantly over the next year, dropping to around $3,200 by late 2018. This period saw market consolidation as many weak hands exited the market.
2020-2021 Bull Run: Bitcoin experienced another surge, fueled by institutional adoption and global economic uncertainty. It reached new all-time highs above $60,000 in April 2021 and peaked at around $69,000 in November 2021. The Covid-19 pandemic played a role in this run, as people looked for alternative investments in uncertain times.
2022 Market Turmoil: Bitcoin faced significant volatility in 2022, with its price dropping below $20,000 amid global inflation concerns, rising interest rates, and major events like the collapse of Terra-Luna and FTX. It ended the year trading in the $16,000-$17,000 range. These events shook the market and caused a significant correction.
2023 Recovery: Bitcoin’s price began recovering in 2023, driven by renewed interest in digital assets and speculation about a potential Bitcoin ETF approval. By mid-year, it had surpassed $30,000, showing signs of stability in a recovering market. The positive sentiment was fueled by hopes of increased institutional investment.
2024 Outlook and Halving Anticipation: Bitcoin’s price trends in 2024 have been shaped by anticipation of the next Bitcoin halving, expected to occur in April 2024. Historically, halvings have driven significant price increases, and many investors are optimistic about a potential bull run leading into and following the halving. Following the April 2024 halving event, Bitcoin saw a significant increase in price, reflecting the historical trend.
Present: Bitcoin’s price continues to fluctuate, influenced by factors like macroeconomic conditions, regulatory developments, and advancements in blockchain technology. As of January 2025, Bitcoin’s price is in the $40,000-$45,000 range, but this can change rapidly.
Is Bitcoin a Good Investment?
Investing in Bitcoin involves risks and rewards. Before you invest in Bitcoin, consider the following:
Benefits of Bitcoin
- Store of Value: Some view Bitcoin as “digital gold,” a store of value resistant to inflation. This is because of the fixed supply of Bitcoin that makes it unable to be manipulated. The limited supply of Bitcoin makes it attractive to investors looking for an asset that is not easily debased by monetary policy.
- High Returns: Bitcoin has shown potential for outsized returns, outperforming many traditional assets. However, it is important to remember that high potential returns come with high risk.
- Accessibility and Liquidity: All that is needed to start using Bitcoin is a Bitcoin wallet, making it easy to access. Additionally, Bitcoins can easily be sold on a cryptocurrency exchange. Bitcoin markets operate 24/7, providing maximum liquidity.
- Independence from Central Authorities: Bitcoin allows users to hold their own private keys, allowing them to become more self-sovereign. This independence gives users greater control over their financial assets.
Risks of Bitcoin
- Price Volatility: Bitcoin’s price is highly volatile, meaning its value can fluctuate significantly. The high volatility is one of the primary concerns for many investors.
- Security Risks: Although Bitcoin is secure, users must be careful as it is possible to lose access to funds if wallet passwords are lost, or if they are stored on a website that is hacked. Proper security practices are necessary to protect your Bitcoin holdings.
- Lack of Regulation: The decentralized nature of Bitcoin means it isn’t regulated, which can increase the risks of scams and fraud. The regulatory landscape of Bitcoin is still evolving, and varies from country to country.
- Irreversibility: If a transaction is made by accident, it can not be traced, and the funds can be lost. This makes it important to double check the transaction details before confirming it.
How to Buy Bitcoin Safely
If you decide to invest in Bitcoin, you need to know how to do it safely.
- Choose a reputable exchange: Buy Bitcoin from a well-established and secure cryptocurrency exchange. Look for exchanges with strong security measures and good user reviews.
- Start small: Do not invest more than you can afford to lose. This is a general investing practice that should be followed when investing in any risky asset.
- Use a secure wallet: Store your Bitcoin in a secure wallet that you control. This will help prevent access by hackers.
- Do your own research: Understand the technology and risks before investing. Don’t just rely on advice from others; educate yourself about Bitcoin.
- Be cautious of scams: Avoid schemes promising unrealistic returns. If it seems too good to be true, it probably is.
What is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving is an event that occurs roughly every four years, where the reward for mining new blocks is cut in half. This is a mechanism built into Bitcoin’s code to control the supply of new coins. When the reward is halved, it slows down the rate at which new Bitcoins are introduced into the market, decreasing the supply and potentially driving up the price. The most recent Bitcoin halving happened in April 2024, and it is the fourth halving in history. The next Bitcoin halving is expected to happen around 2028.
Bitcoin vs Traditional Currency
Bitcoin differs significantly from traditional fiat currency, which is issued by central banks and governments.
Key Differences:
- Decentralization: Bitcoin is decentralized, whereas fiat currencies are controlled by a central authority. This means that Bitcoin is not controlled by a single government or bank, but rather a global network of computers.
- Supply: Bitcoin has a fixed supply, while central banks can increase or decrease the money supply of fiat currencies. The limited supply of Bitcoin helps prevent inflation, whereas fiat currencies are subject to devaluation by increasing the money supply.
- Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions can often have lower fees than traditional banking transactions. Cross-border transactions through Bitcoin can be especially cheaper than traditional methods.
- Global Accessibility: Bitcoin can be transferred globally without the need for intermediaries or third party involvement. Bitcoin can be sent to anyone in the world with a Bitcoin wallet, without any restrictions.
- Reversibility: Bitcoin transactions are typically irreversible, unlike traditional payments that are reversible under certain circumstances. This means that if you send Bitcoin to the wrong address, you might not get it back.
- Regulation: Fiat currencies are backed by a government and are regulated by a central bank. Bitcoin is not backed or controlled by any authority, and therefore is not regulated. The lack of regulation means that Bitcoin users have to be aware of potential risks.
Bitcoin Transactions in Detail
Bitcoin transactions are the transfers of value between Bitcoin wallets on the blockchain. Here is a more in-depth look:
How Bitcoin Transactions Work:
- Transaction Creation: A user creates a transaction with the recipient’s address and amount to send, which is then signed with their private key. The private key is what verifies the user has control over the Bitcoin they are sending.
- Broadcasting to the Network: The transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network for validation by nodes. These nodes verify the transaction according to the rules of the network.
- Mining and Inclusion in a Block: Miners then collect transactions and create a new block. They then do computational work to validate the transactions in that block and add it to the blockchain. This is done using the Proof-of-Work mechanism.
- Confirmation: Once a block is added to the blockchain, the transactions in that block are considered confirmed. Each block that is added on top of the block with your transaction adds an additional confirmation.
Bitcoin Security and Safety
Bitcoin employs strong cryptographic techniques to keep the network secure.
Key Security Measures
- Cryptography: Bitcoin uses cryptographic hashes and digital signatures to secure transactions and prevent counterfeiting. Cryptography ensures that only the owner of the private keys can authorize a transaction.
- Decentralization: The decentralized nature of the network makes it difficult for any one party to control or manipulate the system. No single entity is in charge of the Bitcoin network, which makes it harder for anyone to interfere with the system.
- Blockchain Technology: The blockchain is immutable, meaning that once a transaction is added to the blockchain it cannot be altered. This makes the transactions secure and easy to verify.
- Proof-of-Work: The Proof-of-Work mechanism ensures that it requires extensive computational resources to add a new block to the chain, preventing malicious activity. The cost to attack the network is very high, which protects it from bad actors.
Benefits of Bitcoin
Bitcoin offers many advantages, such as:
- Financial Freedom: Bitcoin gives individuals greater control over their wealth. Users are not reliant on a third party to hold their funds, but rather, are in full control of their own funds.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions often have lower fees than traditional banking systems. This is especially true for cross-border payments.
- Transparency: All Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger for all to view. The blockchain is transparent, allowing all transactions to be verified by anyone.
- Accessibility: Bitcoin can be used by anyone anywhere in the world, allowing for cross-border transactions. All that is needed is a Bitcoin wallet, and an internet connection.
- Scarcity: The fixed supply of 21 million Bitcoins gives it scarcity. The fixed supply is a very important feature for Bitcoin, and is a major reason why many people invest in it.
What is Bitcoin Used For?
Bitcoin has various use cases beyond its use as an investment. Here are some examples of what it can be used for:
Use Cases:
- Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Bitcoin enables users to directly transact with each other, without intermediaries. This direct interaction can be faster and cheaper than traditional systems.
- International Payments: Bitcoin facilitates cross-border transactions with low fees. This is particularly useful in countries with high banking fees and restrictions.
- Online Purchases: Many merchants now accept Bitcoin as a form of payment. Some online marketplaces will accept Bitcoin payments.
- Store of Value: Some use Bitcoin to store wealth due to its limited supply. The limited supply helps ensure that Bitcoin will retain its value over time.
- Remittances: Bitcoin is being used to transfer funds across borders, especially in countries where banking is difficult or not common. This makes it easier for people to send money to their families across the world.
- Supporting Blockchain Networks: Bitcoin helps support a blockchain network by rewarding the miners that process the transactions and secure the network. The Bitcoin network can only function with the support of the miners, who are rewarded with Bitcoin.
Bitcoin For Beginners
If you’re new to the world of Bitcoin, start with these basic steps:
- Learn the Basics: Understand what Bitcoin is, how it works, and its key features. Educate yourself about the technology behind Bitcoin, and not just its price.
- Set up a Wallet: Choose a wallet type that suits your needs and security concerns. There are several options for wallets, and you should find one that fits your needs.
- Buy Bitcoin: Use a reputable exchange to buy a small amount of Bitcoin. Don’t invest too much money when you are first starting.
- Practice Security: Implement good security practices to keep your Bitcoin safe. It is important to follow best practices in order to keep your Bitcoin secure.
- Stay Informed: Keep learning about Bitcoin, as the landscape is constantly evolving. The Bitcoin space is very fast moving, and you should always stay up to date.
Conclusion: The Future of Bitcoin
Bitcoin has undoubtedly transformed the financial landscape, introducing a decentralized, secure, and transparent way to conduct transactions. While its volatile nature and security risks should be taken into account, it also provides the benefit of potential high returns and financial freedom. As Bitcoin continues to develop, it has the potential to reshape the future of money and the financial systems we use today.
The future of Bitcoin is uncertain, but it remains one of the most important cryptocurrencies in the world. The technology behind Bitcoin is constantly being developed, and it is evolving. Many people believe that Bitcoin will be an integral part of the future financial system.
This comprehensive guide should provide a complete understanding of “What is Bitcoin,” along with a complete overview of all of the related aspects that make this digital currency so unique.
Ready to take the next step? Dive deeper into the world of cryptocurrency and explore the possibilities of Bitcoin. Start by researching reputable exchanges, setting up your own secure wallet, and staying informed about market trends. The future of finance is evolving, and now is the time to get involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, also known as a cryptocurrency. It operates on blockchain technology, enabling secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for traditional banking systems or intermediaries. It’s fundamentally digital cash.
How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin runs on a public, distributed ledger called the blockchain. Transactions are grouped into “blocks” and verified by network participants (“miners”). Cryptography secures the network and ensures the integrity of all transactions, preventing double-spending and fraud.
What are the key features of Bitcoin?
Key features include its decentralized nature, a limited supply of 21 million coins, secure cryptographic transactions, transparent blockchain, and global accessibility. This creates a censorship resistant store of value and transfer medium.
What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of verifying and adding new transaction records to the blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems (proof-of-work), and are rewarded with newly created Bitcoins and transaction fees.
How can I store Bitcoin securely?
Use a reputable Bitcoin wallet (hardware, software, or paper). Enable two-factor authentication (2FA). For large amounts, consider a hardware wallet (cold storage) to keep your private keys offline, away from potential online threats.
Is Bitcoin a good investment?
Bitcoin has the potential for high returns, but it is also highly volatile. Thorough research, understanding the risks (market volatility, regulatory changes, security threats), and a diversified investment strategy are essential before considering Bitcoin as an investment.







Pingback: MetaTrader 5 Review: A Powerful Trading Platform CoinFxPro Forex Tools
Pingback: CoinTracker Reviews: Top Crypto Portfolio & Tax Tool CoinFxPro
Pingback: Fair Launch: A Deep Dive into Equitable Crypto Distribution - CoinFxPro
Pingback: A Comprehensive Guide to Cryptocurrency Trading CoinFxPro
Pingback: The Definitive Guide: How to Buy Cryptocurrency in 2025 - CoinFxPro
Pingback: What are Altcoins? A Deep Dive into the World Beyond Bitcoin
Pingback: What is Cryptocurrency? A Comprehensive Guide to Digital Assets
Pingback: What is Kraken Crypto: A Comprehensive Guide CoinFxPro Crypto Tools
Pingback: What is Binance App? A Comprehensive Guide CoinFxPro Trading Tools
Pingback: What is the Coinbase App: A Comprehensive Guide CoinFxPro
Pingback: Top Crypto Exchanges and Apps for January 2025 - CoinFxPro
Pingback: TradingView Review: The Ultimate Tool for Crypto Trading - CoinFxPro
Pingback: History of Cryptocurrency: From Concept to Global Adoption
Pingback: What is Blockchain Technology? A Comprehensive Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: Cryptocurrency Market Crash: Insights and Tips for Investors CoinFxPro
Pingback: The Fee Switch in Crypto: A Deep Dive into Revenue Sharing - CoinFxPro
Pingback: What is a Crypto Wallet? A Complete Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: Cryptocurrency Trading Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide CoinFxPro
Pingback: Understanding Cryptocurrency Regulations and Their Importance
Pingback: What Does Crypto Mining Mean and How Does it Work?
Pingback: What Causes Crypto to Go Up and Down? A beginner's guide
Pingback: What Does Decentralized Mean in Crypto? A Beginner's Guide? CoinFxPro