Table of contents
- 1 What Is a Trading Strategy? A Deep Dive into Forex Trading
- 1.1 Types of Trading Strategies
- 1.2 Forex Trading Strategies for Beginners
- 1.3 Components of a Trading Strategy
- 1.4 How to Create a Trading Strategy
- 1.5 Risk Management in Forex Trading
- 1.6 Technical Analysis in Trading Strategies
- 1.7 The Psychology of Successful Trading
- 1.8 Best Tools for Developing a Trading Strategy
- 1.9 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Is a Trading Strategy? A Deep Dive into Forex Trading
At its core, a trading strategy is a predetermined set of rules and criteria that dictates a trader’s decisions on when to enter, manage, and exit trades. Think of it as your personal roadmap to the financial markets, meticulously crafted to minimize emotional reactions and keep you aligned with your trading goals. Without a concrete strategy, traders are akin to ships adrift without a compass, easily swayed by the ebb and flow of market sentiments, which can lead to costly mistakes. For instance, a trader without a clear exit strategy might hold onto a losing position hoping it will turn around, only to see their losses grow exponentially. A study by DailyFX found that traders who used a consistent trading plan were more likely to be profitable than those who traded randomly based on emotion.
Types of Trading Strategies
The financial markets are vast and diverse, encompassing numerous styles and levels of expertise. This diversity has given rise to a wide array of trading strategies. Understanding the various types can help traders decide which approach is best suited to their individual goals and risk tolerance. Here are some of the popular types of trading strategies:
Scalping
Scalping is an ultra-fast-paced strategy focused on generating small profits from a high volume of trades throughout the trading day. Scalpers typically hold positions for very short durations, often just seconds or minutes. This style demands intense focus, rapid decision-making, and quick reflexes. For instance, a scalper might look to profit from tiny price fluctuations that occur after a significant news release. A trader using this method needs to have a solid understanding of order execution to capitalize on small price changes. Research by brokers indicates that scalping accounts for a significant percentage of daily trading volume in very liquid markets. For example, in EUR/USD during peak hours, scalping activity often forms a substantial part of overall trading volume.
Scalping trading strategy
Day Trading
As its name implies, day trading involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day, aiming to profit from intraday price fluctuations. Day traders may utilize a variety of techniques, such as technical indicators, chart patterns, and news-driven events, to guide their trades. Day traders need to be vigilant and responsive to the market because any position held overnight might be subject to unforeseen events. The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) warns that day trading can be exceptionally risky, especially for individuals who are not well capitalized or don’t have extensive market knowledge.
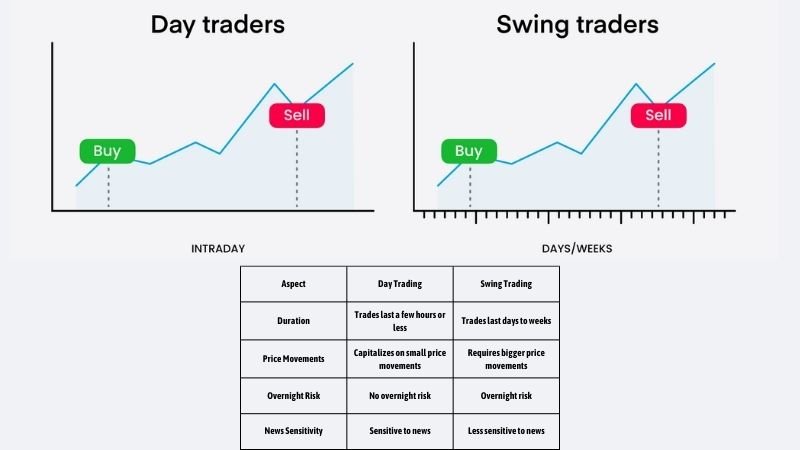
Day trading and swing trading strategy
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for a few days up to a few weeks, seeking to profit from larger price swings. This strategy requires a blend of patience and an understanding of market trends and momentum. Swing traders often use technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points. They might look at moving averages and support and resistance levels. For example, a swing trader might buy a stock after a pullback, anticipating a bounce off a support level. According to a study by Tradeciety, swing trading is a popular style, because it can offer a balance between the time commitment needed by day trading and the long-term approach of position trading.
Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term strategy where positions are held for months or even years, focusing on overall market trends and fundamental factors. This style suits investors with a deep understanding of macroeconomics, geopolitical events, and a long-term investment outlook. Position traders often look at economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates. For example, a position trader might hold a position in a particular currency for several months, believing that the country’s economy will strengthen in the long run. According to research by investment firms, position trading usually requires a robust portfolio and a deep understanding of long term financial trends.
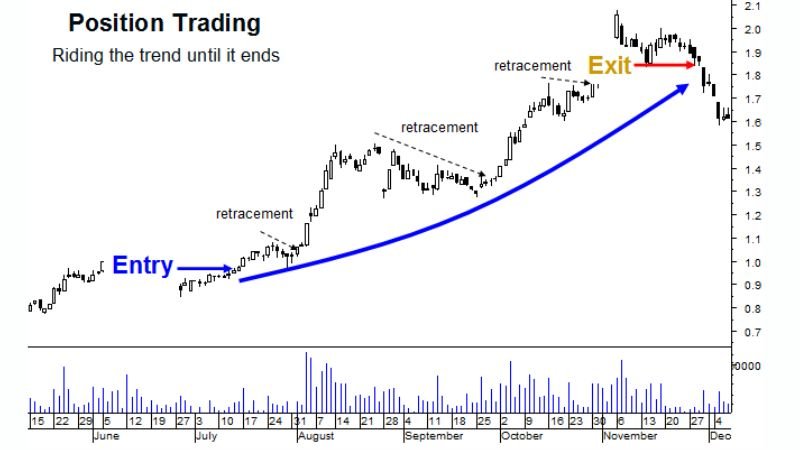
position trading strategy
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic, or ‘algo,’ trading uses computer programs to execute trades based on pre-set rules and parameters. This method removes human emotion from trading decisions and can execute trades with great speed and efficiency. Algorithmic trading often involves complex mathematical models and statistical analysis. For example, high-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algo-trading that is capable of executing thousands of orders in milliseconds. A report by the Bank of International Settlements notes that algo-trading now accounts for a significant portion of total market volume.
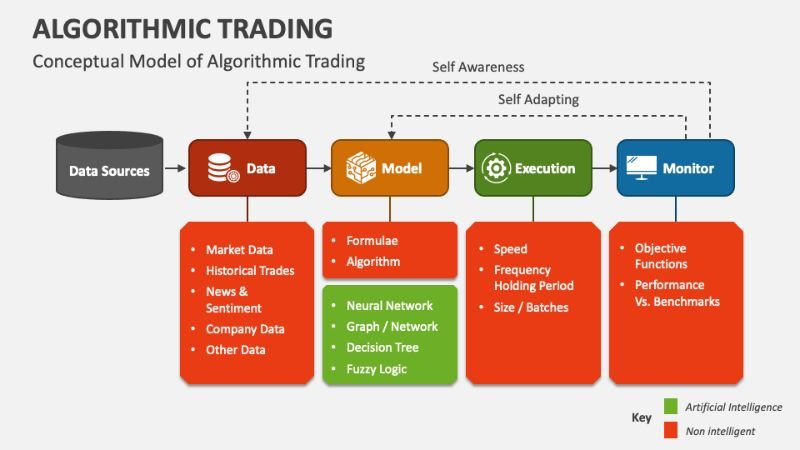
Algorithmic trading
Forex Trading Strategies for Beginners
For those just starting out in the Forex market, simplicity is often the best approach. Here are some beginner-friendly Forex trading strategies for beginners:
Trend Following
Trend following is a straightforward strategy where traders identify an established trend and trade in the direction of that trend. This strategy is less complicated and easier for beginners to understand. Trend following traders use tools like moving averages and trend lines to identify the trend. For instance, if the price of GBP/USD has been steadily rising over the last week, a trend follower would take a long position (buy). According to reports from Investopedia, trend following is a common beginner strategy due to its simple nature.
Breakout Trading
Breakout trading focuses on identifying key price levels (such as support and resistance), and then entering trades when the price ‘breaks out’ from these levels. This strategy is well-suited for those looking to capitalize on price movements after a period of market consolidation. Breakout traders watch for the price to move above a resistance level (for a long trade) or below a support level (for a short trade). For example, a trader might buy a currency pair after it has broken above a defined resistance level. Studies from various trading communities show that breakout trading can be effective but requires careful monitoring of market activity and price patterns.
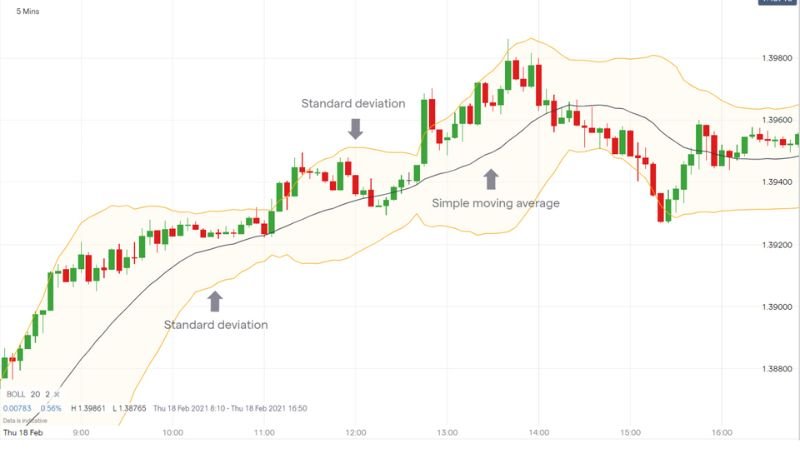
Simple Moving Average (SMA) Strategy
Using a Simple Moving Average (SMA), beginners can identify basic support and resistance levels and make trading decisions based on the average price movements over a selected period. For instance, a trader might use a 20-day SMA to identify potential support levels on an uptrend. When the price dips towards the 20-day SMA, it could signal a good time to buy. A popular strategy for beginners involves looking for crossovers between two SMAs (e.g. 50-day and 200-day), which can signal a change in trend. Many brokerage sites offer tutorials on using moving averages as beginner trading tools.
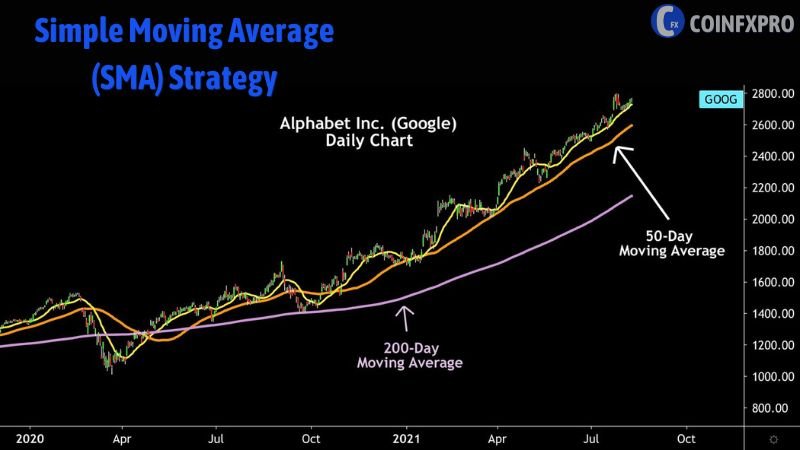
A visual representation of SMA trading.
Example: Suppose you are using a trend-following strategy. If the price of EUR/USD has been consistently rising over the last few days, you might enter a ‘buy’ position, anticipating the trend to continue. Conversely, if the price is trending downwards, you may choose to go ‘short’ or sell.
Components of a Trading Strategy
A robust trading strategy encompasses more than just knowing when to buy or sell. It is made up of several key components of a trading strategy that all need to work together cohesively:
Market Selection
Deciding which markets to trade is a crucial first step. Factors like volatility, liquidity, and your own expertise should significantly influence your choices. For example, if you are a beginner, you may find trading major currency pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/USD more suitable due to their high liquidity and lower volatility compared to exotic currency pairs. Expert opinions often advise focusing on one or two markets initially to become familiar with market behavior.
Entry Rules
These are the specific conditions that must be met before you enter a trade. Entry rules could be based on technical indicators, chart patterns, price action, or a combination of these. For example, an entry rule could be based on a specific crossover of the moving average indicator, or when the price breaks above a particular resistance level. Precise entry rules remove ambiguity and prevent impulsive decisions. A study conducted by trading psychology experts found that having specific entry criteria significantly reduces the risk of emotional trading.
Exit Rules
Exit rules define when you should close your trade, both for profit and for loss. Proper exit rules are essential for locking in gains and protecting your capital. Exit rules can be set using stop-loss orders and take-profit orders. For instance, a trader may set a stop-loss order at a level that limits their risk to 2% of their capital. They may also use a take-profit order based on a risk-reward ratio such as 1:2. Proper exit strategy is a key aspect to successful trading that is highlighted by numerous sources on trading.
Position Sizing
Position sizing determines how much of your trading capital you will risk on a single trade. This is a vital risk management component which is crucial for preventing substantial losses. For instance, a trader might use a percentage-based model where they risk a fixed percent of their total capital per trade (e.g., 1-2%). By implementing appropriate position sizing, traders can avoid taking losses that are too large. According to risk management research, proper position sizing is critical for the long-term sustainability of any trading strategy.
Risk Management Parameters
These parameters define how much risk you are willing to take on a per-trade basis and how you will react in the event of losing trades. This typically involves setting stop-loss levels and setting the overall risk that is acceptable for your portfolio. For example, you might set a risk limit to never risk more than 2% of your total capital on a single trade. Trading forums often advise that sticking to predefined risk parameters is critical for maintaining capital.
Backtesting
Before deploying your strategy in a live market, it’s essential to test it on historical data. This process, called backtesting, helps you understand your strategy’s potential performance under various market conditions. It can also help to refine the rules before using the strategy in the real market. Backtesting involves applying your trading rules to historical price data to simulate how the strategy would have performed over a specific time. Many platforms offer backtesting features, which allow traders to see metrics like win rates, maximum drawdowns, and the average return. Studies by quantitative analysts show that strategies that perform well in backtests often have a higher chance of success in live trading. However, it is worth noting that backtesting can only provide an estimate. The actual results may vary because of the differences in market conditions and slippage.
How to Create a Trading Strategy
Creating your own how to create a trading strategy can seem daunting, but when broken down into logical steps, it becomes a manageable process:
- Define Your Goals: Start with a clear understanding of what you want to achieve with trading. What is your risk tolerance, and how much capital are you looking to commit? Are you looking for long-term wealth building or short-term gains? Setting clear financial goals will guide your strategy. For example, a trader who seeks capital preservation may adopt a less risky strategy than a trader looking for quick profits. Financial advisors often emphasize the importance of clear objectives for any investment strategy.
- Research and Choose Your Trading Style: Decide which of the various trading styles (scalping, day trading, swing trading, position trading, etc.) aligns best with your personality, time commitment, and financial goals. If you have limited time, scalping might not be the most suitable strategy. If you have a more long term view on the market, then you may prefer position trading. Different trading styles have different requirements and risk profiles. According to trading psychology studies, matching a trading style with your personality can boost success.
- Select Your Market: Focus on one or two markets that you understand well rather than trying to trade them all at once. This could be Forex, stocks, commodities, or cryptocurrencies. If you are familiar with a certain sector of the market then it may be better to stick to that market to begin with. Trading experts generally recommend gaining mastery in a few markets rather than spreading oneself too thin.
- Develop Entry and Exit Rules: Based on the strategy chosen, define precise rules for when to enter a trade and when to exit, whether for profit or loss. Entry and exit rules should not be arbitrary but based on technical analysis, price patterns or some clear criteria. A rule might be to enter when a certain indicator such as the RSI or MACD crosses over, and then exit when the price reaches a level predetermined by a risk reward ratio. Many trading books stress the importance of specific and clear rules.
- Implement Risk Management Parameters: Decide how much you are willing to risk on each trade and establish rules for how you will manage losses. Setting a fixed stop loss at a certain percentage of capital or level in pips is an effective way to manage risk. This includes risk per trade, overall risk allocation, and maximum drawdown. According to risk management experts, predefined risk limits can significantly protect your trading account.
- Backtest Your Strategy: Thoroughly test your strategy on historical data to evaluate its performance and refine its parameters. This process will help determine how the strategy may have performed in past market conditions. This step is critical for verifying a trading strategy’s potential. A backtest will give the trader a good idea about its win rate, risk reward and other performance metrics. Quantitative analysts emphasize backtesting as a crucial step in strategy creation.
- Refine Your Strategy: Based on the results of backtesting and early live trading, fine-tune your strategy for optimal results. It is a mistake to assume your strategy will perform perfectly after the backtesting. Refining will allow the trader to account for unexpected conditions. Strategy refinement is an iterative process that is often needed. Trading experts always advise that continuous evaluation and refinement are essential for long-term success.
- Practice: Start by practicing with a demo account before risking real capital. This will help you get a feel for trading and allow for error without actually losing any money. Most brokerages offer demo accounts, which can be used to practice strategies. Demo trading allows you to become familiar with the software and market dynamics. According to trading communities, practicing with a demo account is the first step for any beginner.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
No trading strategy is complete without robust risk management in Forex trading. The Forex market is notorious for its volatility, so proper risk management is not just important; it’s vital for survival.
Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are the most crucial tool for limiting potential losses. They automatically close out a trade when the price reaches a pre-determined level. A stop-loss order is a must have for any trading strategy, and is crucial for capital preservation. For instance, if you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, you might place a stop-loss order at 1.0950, limiting your loss to 50 pips if the trade goes against you. Brokerage sites and experts on risk management emphasize that using stop-loss orders are essential for managing your trading risk.
Position Sizing
By carefully managing position sizes, you can limit how much of your capital is at risk on each trade. This strategy helps traders avoid overexposure to any single trade, by ensuring that no trade will completely wipe out a trader’s capital. This involves calculating your trade size based on your stop-loss level, and risk appetite. For example, if your account is $10,000 and you are willing to risk 2% per trade and your stop-loss is 50 pips, you would calculate the position size that would represent a $200 loss. Risk management research often highlights that proper position sizing is a key factor in traders’ success.
Risk-Reward Ratio
Aim for a risk-reward ratio that is favorable. This means your potential profit should ideally be greater than your potential loss. A risk-reward of 1:2 would mean that for every one dollar risked, you are targeting a profit of 2 dollars. For instance, if you are risking 50 pips to gain 100 pips, you have a risk-reward ratio of 1:2. Many successful traders suggest that consistently aiming for a good risk-reward ratio is a recipe for long term success, even if win rate is lower.
Diversification
Spreading your trades across different currency pairs and/or markets can help mitigate risk. By not investing all your capital in one market you will reduce the risk of market specific events wiping out your capital. This approach can prevent total portfolio losses if one particular market performs poorly. Financial advisors often recommend a diversified portfolio to minimize overall investment risk.
Avoiding Over-Leveraging
Leverage can magnify both profits and losses. Always trade with leverage responsibly, taking into account your risk tolerance. While leverage allows for the potential of greater gains, it can also lead to very large losses. It is crucial to understand how leverage works before using it in your trading. Many brokers offer leverage, but using it cautiously is a must for beginners. Many trading tutorials warn about over-leveraging because it can lead to devastating losses.
Example: If you have a trading account of $1000, you might decide that you’re only willing to risk 2% on any one trade, which would mean limiting your risk to $20. A stop-loss order and carefully sized positions are the tools to achieve this.
Technical Analysis in Trading Strategies
Technical analysis in trading strategies involves studying past price movements to try and predict future trends. It is a powerful tool used by traders of all experience levels.
Chart Patterns
Patterns like triangles, wedges, head and shoulders, and flags are used to indicate potential price movements. Chart pattern analysis forms the basis for many trading strategies. A trader may look for a bullish flag pattern to potentially take a long position. Technical analysis books often provide detailed descriptions of these chart patterns, including entry and exit strategies. The use of chart patterns as a trading strategy is widely supported in the technical analysis field.
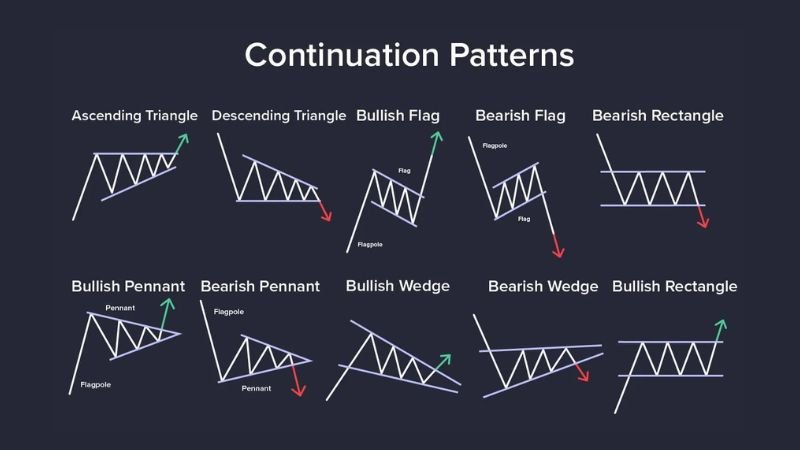
A visual representation of chart patterns.
Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on price and volume, used to generate trading signals. Common examples include Moving Averages, RSI, MACD, and Bollinger Bands. For example, a trader may use the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to gauge overbought or oversold conditions. Technical indicators are key instruments in technical analysis, used to get signals to enter and exit trades. Many traders use a combination of technical indicators to gain greater signal confirmation.
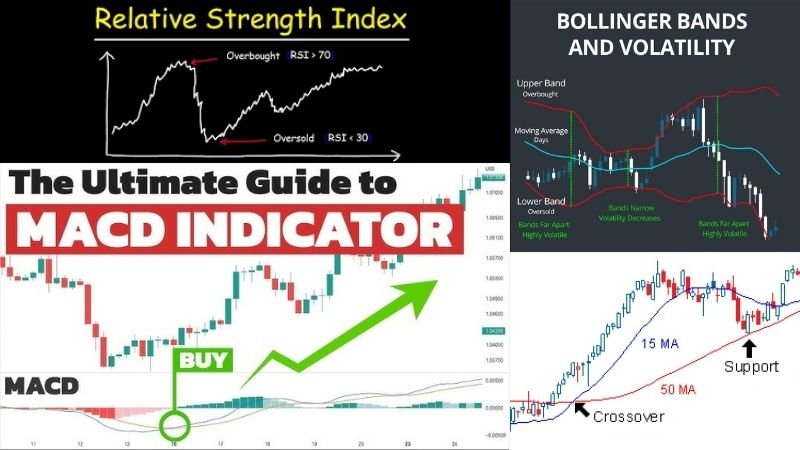
A visual representation of technical indicators.
Trendlines
Drawing trendlines on price charts can help identify trends and potential areas of support and resistance. A trendline drawn on the lows of the chart can be used as a support level. A trendline drawn connecting the highs can be used as resistance. The use of trend lines can be a simple way of identifying potential trade areas. Numerous sources on technical analysis highlight the use of trend lines for this purpose.
Example: A trader might notice a ‘double bottom’ pattern on a price chart. This pattern often signals the end of a downtrend and the start of an upward trend. Based on this analysis, the trader might enter a ‘buy’ position.
The Psychology of Successful Trading
The psychology of successful trading is often underestimated, yet it can make or break a trader. Emotional discipline is critical for long-term success in the markets.
Fear and Greed
These two emotions can lead to impulsive, poorly-thought-out trading decisions. A strong trading strategy can help mitigate the influence of these emotions. Fear can make traders close out trades too early, and greed can make traders hold losing positions hoping that the market will reverse. Trading psychology experts often stress the importance of emotional control. Studies show that the majority of trading mistakes are caused by poor emotional control.
Patience
Successful trading requires patience. Not every day will be a winning day, so avoiding over-trading and focusing on the strategy’s rules is crucial. Traders need to wait for a setup that aligns with their rules before entering a trade. Patience means waiting for the right opportunity rather than forcing a trade. Trading books and coaches often say that patience is a critical virtue for profitable trading.
Discipline
Sticking to your trading strategy, even when it’s difficult, is critical for long-term success. This involves maintaining composure during winning and losing streaks. Discipline also means adhering to the strategy’s rules consistently. The importance of discipline is constantly highlighted by trading educators. Discipline means following the plan regardless of whether you just had a losing streak or a winning streak.
Dealing with Losses
It’s essential to accept that losses are a part of trading, learn from them, and move on rather than letting them influence future decisions. It is important to accept trading losses as a part of the process, and use them as learning tools. A trader must not take revenge trades, but rather should review the process and see what went wrong. Trading psychology resources indicate that handling losses gracefully is a key attribute of successful traders.
Example: If you have a losing trade, instead of immediately going for a revenge trade, a disciplined trader would review the trade and see where they might have made a mistake. Perhaps they didn’t follow their strategy properly, or perhaps their strategy needs some adjustment.
Best Tools for Developing a Trading Strategy
Developing and testing a trading strategy often involves a variety of tools. The best tools help you make informed decisions and efficiently monitor your trades. Here are some of the best tools for developing a trading strategy:
Trading Platforms
Platforms like MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and TradingView offer advanced charting tools and indicators, and are essential for executing trades. These platforms also offer the ability to use automated strategies. Many of these platforms offer various technical indicators and tools to analyze market data. Popular online communities and courses recommend familiarizing yourself with at least one trading platform.
Tradingview trading platforms.
Economic Calendars
Economic calendars can help traders stay informed about upcoming economic releases that could affect their trades. These calendars list the times of economic releases and their projected impacts on the market. Traders use this to time their trades or avoid trading during high impact news releases. Many trading resources strongly advise that traders be aware of upcoming releases.
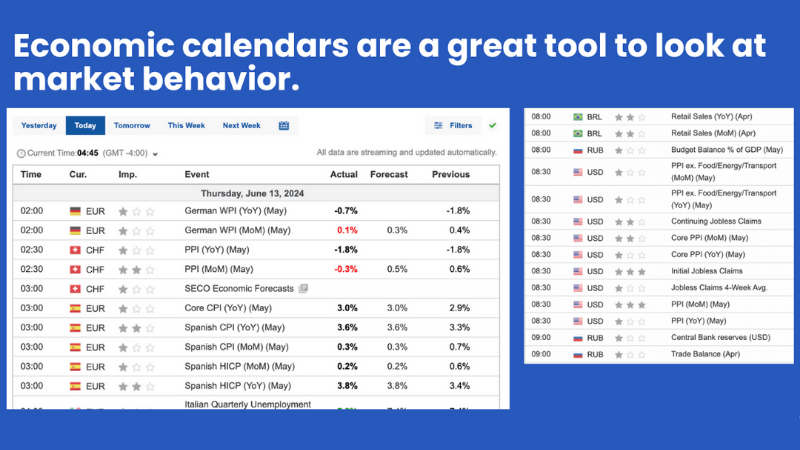
Economic calendar.
Backtesting Software
Software like Forex Tester allows you to test your strategy on historical data and see how it would have performed in the past. These tools can be useful for refining a trading strategy before you use real money to trade. Traders can use backtesting software to understand the potential of their strategy, and to adjust parameters if needed. Numerous sites specializing in trading emphasize the importance of backtesting as a key component of strategy development.
Demo Accounts
Most brokers offer demo accounts, which allow traders to practice their strategy without risking real money. Traders can practice trading strategies and also become familiar with the user interface of different brokers’ platforms. The availability of demo accounts allows beginners to test and experiment with strategies without putting any capital at risk. It is often suggested that demo trading should be an initial stage for traders who are new to the market.
Example: Using a platform like TradingView, a trader can backtest their strategy by applying various indicators on historical data to see how they performed. This helps them refine the rules of their strategy and improve their trading skills.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a trading strategy?
A trading strategy is a comprehensive plan with specific rules that guide traders’ decisions. It dictates when to enter, manage, and exit trades, minimizing emotional decisions and promoting consistent, profitable results in the markets. It is essential for achieving successful trading goals.
What are the main types of trading strategies?
Common trading strategies include scalping (very short-term), day trading (intra-day), swing trading (days to weeks), position trading (long-term), and algorithmic trading (automated). Each style suits different risk profiles, time commitments, investment objectives and trading personality traits. They exist across diversified strategies.
How do I create a trading strategy?
Creating a strategy involves setting clear financial goals and then determining any trading style. Develop precise entry/exit rules. Apply stringent risk management, and backtest your strategy thoroughly using historical data before risking any real capital in live trading sessions.
What are the key components of a trading strategy?
Essential components include market selection (which assets to trade), clear entry/exit signals, robust risk management (stop-losses, etc.) and optimized position sizing. Continuous Strategy improvement is key and backtesting is just an element. These elements create a systematic, effective approach.
Why is risk management important in Forex trading?
Risk management is crucial in Forex trading to protect your trading capital. It involves setting stop-loss orders, managing position sizes, and diversify the protfolio. Preserving capital allows for long-term trading and minimizes large losses. This ensures sustainability of financial success.
What tools can help develop a trading strategy?
Essential tools include advanced trading platforms like MetaTrader, backtesting and optimization software, economic calendars for fundamental analysis, and demo accounts for risk-free practice. These tools facilitate thorough analysis, strategy testing, and refinement for different market conditions. Tradingview is another great option.













Pingback: Best Forex Brokers for January 2025: A Comprehensive Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: AI Wallets Explained: Features, Benefits, and Investment Strategies
Pingback: ChartPrime Review: Is It the Ultimate Trading Tool? CoinFxPro
Pingback: The Professional Trader's Guide to Forex Risk Management - CoinFxPro
Pingback: What is Kraken Crypto: A Comprehensive Guide CoinFxPro Crypto Tools
Pingback: What is Binance App? A Comprehensive Guide CoinFxPro Trading Tools
Pingback: MetaTrader 5 Review: A Powerful Trading Platform CoinFxPro Forex Tools
Pingback: How Bubblemaps Crypto Tools Revolutionize Blockchain Analytics