Table of contents
- 1 What Does Decentralized Mean in Crypto?
- 1.1 What Does Decentralized Mean in Crypto?
- 1.2 Understanding Decentralization in Blockchain
- 1.3 Benefits of Decentralization in Crypto
- 1.4 Challenges and Risks of Decentralization
- 1.5 Decentralization: Its Practical Uses in Crypto
- 1.6 Future of Decentralization in Crypto
- 1.7 FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
- 1.8 Conclusion
- 1.9 Further Reading
- 1.10 References & Sources
What Does Decentralized Mean in Crypto?
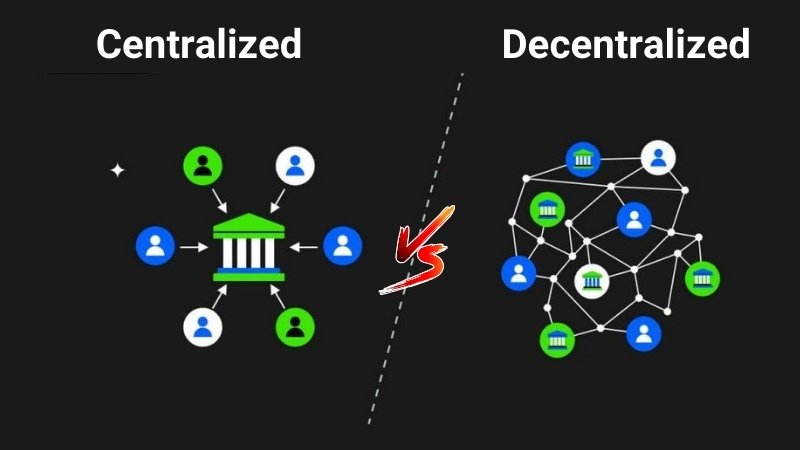
In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrency, “decentralization” is a foundational concept. It’s more than just a buzzword; it’s the core principle that distinguishes cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum from traditional financial systems. But what does decentralized mean in crypto, exactly? In simple terms, it means that no single entity, like a bank or government, controls the network or the assets within it. This is a radical departure from centralized systems, where a central authority has ultimate power.
What Does Decentralized Mean in Crypto? Decentralization in crypto means that control and decision-making power are distributed across a network of participants rather than being concentrated in a single entity (like a bank or government). This ensures no single point of failure or control, enhancing security, transparency, and censorship resistance.
Decentralization is the backbone of blockchain technology, the underlying technology for most cryptocurrencies. It’s what gives these digital assets their unique properties, such as security, transparency, and resistance to censorship. This article will delve into the intricacies of decentralization, exploring its benefits, challenges, and real-world applications.
Differents between centralized and decentralized
Key Takeaways:
- Decentralization distributes control across a network, eliminating single points of failure.
- It enhances security, transparency, and censorship resistance in cryptocurrencies.
- Blockchain technology, through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, enables decentralization.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and smart contracts are revolutionizing financial applications.
- Challenges include scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and user responsibility.
What Does Decentralized Mean in Crypto?
In essence, the meaning of decentralized in crypto is the way in which power and control are distributed across a network instead of being centralized in one place. This means no one person, company, or government can unilaterally decide what happens on the network, change its rules, or seize control over how money flows. It’s like a common, public ledger that everyone can see and check, but nobody can corrupt.
Architectural Decentralization
This means the physical structure of the network. In a truly decentralized system, there are many, many nodes (computers) worldwide sitting on the network, and your job to shut it down or attack it becomes that much harder. The multiple points of delay, outage, and impact mean that there is no single point of failure. If one node goes down, the network doesn’t even blink.
Political Decentralization
What this means, as you probably gathered, is that there is no singular person or group that can dictate the rules or future development of the cryptocurrency. Decisions are typically made through mechanisms of community consensus, whereby voting on proposed changes is done through users and developers.
Logical Decentralization
This is in reference to the decision-making process being distributed. Disagreement should not stall the network, and forks (chain separation) ensure the network continues to function. This provides a non-destructive framework for experimentation and adaptation.
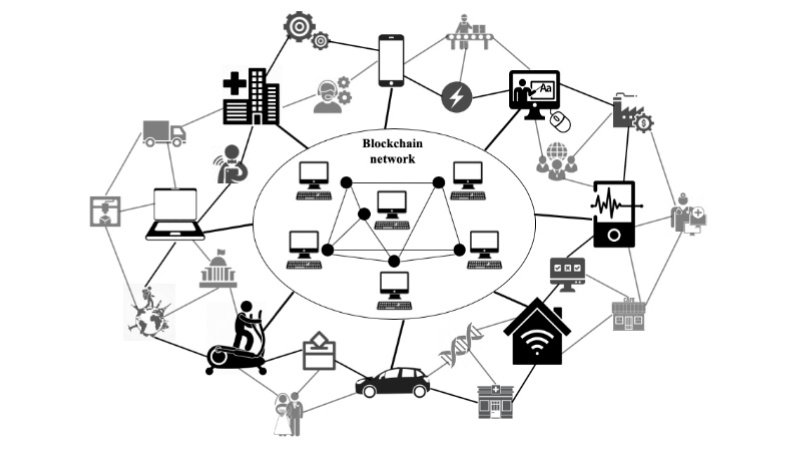
Diagram of decentralized blockchain architecture
Understanding Decentralization in Blockchain
Blockchain technology is the key to achieving decentralization. A blockchain is basically an electronic transaction ledger that is shared and replicated across the complete computer system network on the blockchain. Each block on the chain has several transactions, so when there is a new transaction on the blockchain, a record of that transaction is added to every participant’s ledger.
Nodes & Validators: The computers that run on the network Their role is to confirm transactions, ensuring that each is proper and meets the network’s specifications. With such thousands and even millions of nodes, we are making it very hard for them (the network) to be controlled by any single entity.
Consensus Mechanisms
These are rules that define how the network agrees on the validity of transactions. They are essential for maintaining the accuracy of the blockchain and deterring fraud.
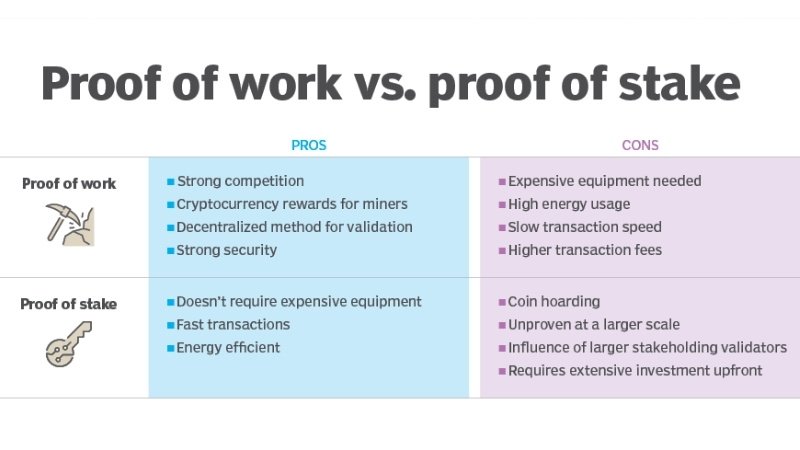
Proof of Work (PoW)
That is the system upon which Bitcoin operates. Miners (nodes) race to solve complex equations. The winning miner gets to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain and earn a reward in newly minted Bitcoin. This is resource-intensive, leading to the network being extremely costly to attack.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
This is the method Ethereum is following (through its evolution to Ethereum 2.0). They stake their cryptocurrency as collateral instead of relying on computational power. Validators are selected at random to prepare and attest blocks. This system is far more energy efficient than PoW.
Benefits of Decentralization in Crypto
Increased Security
Security is among the primary advantages of decentralization. Hackers do not target the entire network due to the lack of a single point of centralization. A distributed blockchain, operating on distributed consensus methods like proof-of-work (PoW), proof-of-stake (PoS), etc., makes it nearly impossible for an attacker to “take over” the network. Normally, the costs are prohibitive and impractical, and an assault would need a hostile actor to control most of the computational power of the network (in the PoW case) or most of the cryptocurrency in play (in the PoS case).
Censorship Resistance and Financial Freedom
Decentralized crypto assets provide a level of financial freedom that cannot be obtained in traditional financial systems. Even governments and financial organizations typically cannot easily freeze your assets, limit transactions, or prevent you from withdrawing cash. In countries that have weak banking systems or severe capital controls, this is especially important. According to the Cambridge Center for Alternative Finance, Bitcoin adoption is growing in countries with high inflation or tight capital controls.
Openness and confidence
Since most blockchains are open source—that is, anyone could read the source code, and the validity of any transaction can be verified. This openness cultivates trust because consumers can verify the system themselves without reliance on any single central authority.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) & Smart Contracts
Also, decentralization extended our vision to the establishment of decentralized finance (DeFi), a paradigm shift for the financial service provider ecosystem enabled by blockchain technology. DeFi apps like Aave, Uniswap, and MakerDAO allow users to borrow, lend, trade, and earn interest on their assets without a bank or other traditional financial institution.
Smart contracts, automatically executed contracts based on programming code, are also contributing towards automating the transaction and contract execution process and thereby reducing dependence on third parties. This lowers transaction costs, enhances transparency, and reduces risk.
Challenges and Risks of Decentralization
Decentralization is pretty, yet it has some problems and risks.
Scalability Issues
However, decentralized networks can sometimes be slower and less efficient than their centralized counterparts. This is because each transaction has to be confirmed by multiple nodes in the network, which requires time and ecomin power. In its early days, Bitcoin struggled to cope with unprecedented levels of transaction volume. But hey now, we’re getting somewhere! For this, a few innovative solutions like Layer 2 scaling solutions (like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Optimistic Rollups for Ethereum, etc) are being developed.
Regulatory Uncertainty
But governments globally are still trying to work out how to regulate decentralized cryptocurrencies and DeFi platforms. Because there’s no central authority, it’s difficult to apply traditional financial regulations. The ongoing tussle between the SEC and various DeFi platforms is revealing that there is some uncertainty around the rules.
User Responsibility
Decentralization puts more responsibility in the hands of users, so understand the risks. Similar to if you lose your private keys (the cryptographic keys that allow you to control your crypto assets), you will lose your funds forever. And that’s why it is so important to keep your crypto in a secure wallet and know how to handle your keys properly.
A decentralized vs. centralized security trade-off
Decentralization: Its Practical Uses in Crypto
Bitcoin (BTC)
Bitcoin is the original and most widely used distributed cryptocurrency that functions both as a digital store of value and a means of payment. Its decentralized nature enables it to resist manipulation and censorship.
Ethereum (ETH)
And on Ethereum, you can write smart contracts and dApps. Its second dynamic ecosystem offers a wide range of applications from DeFi systems to NFT marketplaces. The Ethereum Foundation material reveals some of the decentralization commandments that Ethereum provides.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Decentralized exchanges, or DEXs like Uniswap and PancakeSwap, allow users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with one another without a middleman. This provides additional privacy and control of funds. You may want to compare these with some of the top crypto exchanges.
Decentralized Storage & Web3 Projects
Projects such as Filecoin and IPFS are developing distributed storage systems in which people can offer their spare storage for rent and be compensated in bitcoin. These efforts fall under the wider Web3 movement, which aims to create a more decentralized and user-owned internet.
Future of Decentralization in Crypto
The future of decentralization in cryptocurrencies is bright, despite having a few unknowns. Ethereum 2.0 When Ethereum 2.0 is released, it will have multiple positive effects, including its transition to Proof of Stake (PoS) and improved scalability. The second major increase would come from advances in blockchain technologies themselves—sharding and zero-knowledge proofs—and should help scale and secure distributed networks even further.
Governance tokens and these Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), companies controlled by code at the direction of community members, are also catching on. DAOs are set to disrupt how many different sectors make decisions and govern themselves.
Even so, the rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) presents a potential hurdle. Central Bank Digital currencies (CBDCs) are digital currencies issued and regulated by the central banks of the world. Although they may in some circumstances offer increased financial inclusivity and efficiency over existing ones, they would really just be centralized and compete with distributed cryptocurrencies. Bank of International Settlements (BIS) Research on Digital Currencies and CBDCs
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions
What does decentralized mean in crypto?
Decentralization means no central entity controls transactions or decision-making. Instead, a decentralized network of nodes (individual computers) helps in validating and recording transactions that make it more secure, transparent, and less susceptible to censorship. That’s the beauty of this system, as it prevents fraud, minimizes the use of intermediators, and, most importantly, keeps the financial ecosystem trustless and tamper-free.
Why is decentralization important in blockchain?
Decentralization adds security to blockchain. There are no intermediaries in peer-to-peer transactions, which is really cool because it allows for inclusivity and transparency. It uses a network of nodes to decentralize power, yield trustless systems, and ultimately create a fairer, more inclusive digital economy for all participants.
Bitcoin is 100% decentralized, right?
What are some of the disadvantages of decentralization?
The disadvantages of decentralization are the expense of slower transactions, scalability issues, and regulatory ambiguity. Users need to safeguard private keys since they will lose access to their assets permanently if lost. Decentralized networks are yet more computationally resource-intensive and thus energy-intensive, as well as difficult to govern effectively.
How does decentralization impact financial freedom?
Decentralization helps that users have the liberty to access and encounter financial services with no boundaries. It is like the protection against government censorship, asset freezes, and transaction restrictions. DeFi provides you with borderless and peer-to-peer transactions, granting you more financial freedom and independence in regions with restrictions.
Conclusion
Decentralization helps that users have the liberty to access and encounter financial services with no boundaries. It is like the protection against government censorship, asset freezes, and transaction restrictions. DeFi provides you with borderless and peer-to-peer transactions, granting you more financial freedom and independence in regions with restrictions.
Further Reading
- What Is Blockchain Technology? – A deep dive into the foundational technology behind cryptocurrencies.
- What is Cryptocurrency? – A comprehensive introduction to the world of digital currencies.
- Cryptocurrency Regulations – Explore the evolving legal landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies.
- Governance Tokens – Learn how these tokens are shaping the future of decentralized organizations.
- What is a Crypto Wallet? – Understand the different types of wallets and how to securely store your crypto assets.
References & Sources
- CoinDesk – Research on decentralized finance.
- Ethereum Foundation – Ethereum decentralization insights.
- Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance – Crypto adoption & decentralization data.
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) – Information on crypto regulation.
- Bank for International Settlements (BIS) – Research on digital currencies and CBDCs.