Table of contents
What Does Crypto Mining Mean?
Crypto mining is a term that gets thrown around a lot in the world of cryptocurrency, but what does it actually mean? At its core, crypto mining is the process of verifying and adding new transaction records to a public, distributed ledger known as a blockchain. This process is essential for the security and decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others.
It is quite important, due to crypto mining’s ability to maintain blockchain integrity. A deficiency of miners would make it impossible to securely include new transactions, and the network could be vulnerable to attacks such as double-spending. So miners are critically important; they are the backbone of the network.
How Does Crypto Mining Work?
Consensus Systems of Thought
You learn the concept before entering into mining with the help of consensus techniques. This is the process of systems that are the rules used to govern the operational and validation of transactions through the blockchain. The two most common systems are
- Proof of Work (PoW): This is the consensus algorithm that Bitcoin employs and is the original. Miners solve complex computational puzzles in order to validate transactions and create new blocks on the network. The first miner that solves the puzzle gets to write the new block and receives freshly minted bitcoin.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In this approach, validators who were chosen to create new blocks were determined by how much money they “staked,” or held and agreed not to touch. In general, PoS requires lower energy than PoW.
PoW vs. PoS:
| Feature | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | High | Low |
| Security | Highly secure, proven track record | Secure(growing adoption and testing) |
| Participation | Requires significant computing power | Requires staking coins |
Step-by-step mining technique
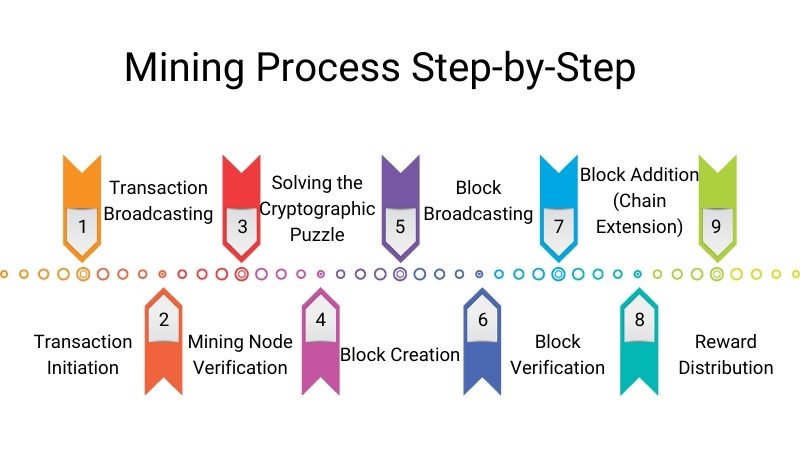
In particular, the crypto mining process involves the following phases in PoW chains:
- Transaction Initiation: A user initiates a transaction, sending cryptocurrency from one address to another.
- Transaction Broadcasting: The transaction is propagated over the network and added to a pool of unconfirmed transactions, called the mempool.
- Mining Node Verification: Mining nodes are powerful computers that select these unconfirmed transactions from the mempool.
- Solving the Cryptographic Puzzle: Miners compete to solve a complex cryptographic puzzle. This means finding a nonce—a random number—which, when added to the data of the block and run through a hash function, produces a hash that matches certain criteria—e.g., that has a certain number of leading zeros. how computationally demanding this is.
- Block Creation: When a user has confirmed their transaction, it is then available for miners to include in the next block. The first one to find a feasible solution (i.e., validate the transaction) builds out a new block and broadcasts it to the network of miners.
- Block Broadcasting: The new block is broadcast to the network.
- Block Verification: Other nodes in the network verify the validity of the new block and the included transactions.
- Block Addition (Chain Extension): Once validated, the new block is added to the chain, and the transactions recorded in it are considered confirmed. Chain extension, Add block
- Reward Distribution: The effective miner that contributed the block is paid transaction fees and a block reward—newly minted bitcoin.
Mining Hardware and Software
Different types of mines and different coins have different requirements. Here are the most commonly occurring types broken out:
- ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits): These are specialized chips designed for mining certain cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin). They are only capable of mining specific algorithms and are expensive, but they are the most powerful and efficient option available to PoW miners.
- GPUs (Graphics Processing Units): GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) were originally intended for gaming but are also used to mine a few cryptocurrencies. But ASICs are less power efficient when they offer more flexibility than ASICs.
- CPUs (Central Processing Units): CPUs (central processing units) are generally not powerful enough to be profitable with most cryptocurrencies, although possibly some very new or niche coins can be made to work for tax purposes but are normally unprofitable.
Miners also need software to connect to the network and monitor the mining process. Some of the fairly common options include:
The Economics of Crypto Mining
Mining Costs & Profitability
Mining isn’t free! It comes at a number of costs:
- Electricity Costs: This is typically the largest expense. Mining machines, especially ASICs, have a lot of power consumption
- Hardware expenses: The initial capital cost may be considerable, particularly for high-performance ASICs, but the cost of mining hardware can be broken down into four components.
- Cooling Costs: A mining farm generates a ton of heat and therefore requires cooling systems to prevent it from becoming hot and thus further increase the electricity consumption.
- Maintenance & Repair: Hardware can fail and need fixing or replacing.
To ascertain if mining is lucrative, miners must calculate their Return on Investment (ROI). This means balancing factors like:
- Hash rate of the hardware
- Electricity cost
- Network difficulty
- Current cryptocurrency price
- Block reward
According to the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (CCAF), Bitcoin mining consumed approximately 105 TWh of electricity per year in 2023.
Rewards & Incentives
In order to incentivize miners to participate in, rewards can be used:
- Block Rewards: The most important earnings for mining. When a miner successfully adds a block to the network, they receive some fixed amount of newly minted cryptocurrency. The initial Bitcoin block reward was 50 BTC; it halves approximately every 4 years (a process sometimes referred to as a “halving”). The current block reward (as of 2024) is 6.25 BTC.
- Transaction Fees: Miners also receive the transaction fees associated with the transactions they have added in a block.
Halving events really impact miners’ income because the block reward is cut in half. This is designed to contribute to the deregulatory proceedings of inflating the cryptocurrency.
Environmental Impact of Crypto Mining
Energy Consumption & Sustainability
Especially Bitcoin mining, energy used by PoW mining has become a serious concern. Mining eats up a lot of electricity because it requires a lot of computing power.
According to 2023 statistics, the Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Usage Index (CBECI) estimates the annual energy consumption of Bitcoin mining equivalent to that of small countries such as Argentina or the Netherlands.
Initiatives for Green Mining
Crypto mining’s environmental impact has pushed the development of ever-more-environmentally-friendly mining approaches:
- Renewable Energy Sources: To further combat their carbon footprint, numerous mining efforts are branching out to incorporate solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, and other forms of renewable energy. For example, projects such as Tesla exploring Bitcoin mining using green energy have started.
- Hydropower Mining: Some regions with abundant hydroelectric power, such as parts of China (before the ban) and Iceland, have established centers for crypto mining.
- Carbon Offsets: Some mining businesses are investing in carbon offset projects to mitigate their ecological impact.
Challenges and Risks in Crypto Mining
Network Hashrate and Mining Difficulties
Mining Difficulty: Design-wise, most cryptocurrencies employ a “mining difficulty adjustment” mechanism. This adjusts the difficulty of the cryptographic puzzle automatically, based on the network’s total computing power—hashrate. When more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, thus increasing the hashrate and hardening the search for a valid block. This ensures a steady rate of addition to the chain—about once every ten minutes for Bitcoin.
Network Hashrate: The total combined computational power of all miners on the network.
51% Attack & Security Issues
The 51% attack is a potential vulnerability of PoW blockchains. If one person or group owns over 50% of the hashrate of the network, they can theoretically modify the blockchain by, for instance, double-spending cash or preventing the approval of fresh transactions. Although executing on a large, well-established network like Bitcoin is typically extremely difficult to accomplish and expensive to do, this is still a major security issue.
Regulatory and legal concerns
Global legality: The legality of crypto mining varies widely around the world. Yet some countries have been more friendly, with some explicitly outlawing crypto mining. For instance:
- Bans: China, Kazakhstan (with some restrictions)
- Friendly Jurisdictions: Texas (USA), Canada, El Salvador
Laws are never static, so miners need to remain attentive to the legal framework of their jurisdiction.
Future of Crypto Mining
Crypto Mining Evolution: Will we shift from PoW to PoS?
One of the more energy-efficient consensus processes is PoS, and it seems to be one of the trends that is bound to continue. A great example of blockchains changing this dynamic is Ethereum’s switch from a PoW consensus model to PoS (completed with “The Merge” in 2022). Most newer cryptocurrencies are launching with PoS from the get-go.
Future Innovations in Mining Technology
Technological advances can affect future mining very differently. This covers:
- More efficient ASICs
- New mining algorithms
- Quantum Computing: The increasing threat that quantum computing poses to the security of various cryptographic systems can potentially harm the security of crypto mining from a long-term perspective. However, quantum-resistant techniques are also being developed.
Will it still be profitable to mine cryptocurrencies?
Predicting the long-term viability or prosperity of crypto mining is difficult as it depends on a number of factors such as legal reforms, tech advances, and crypto prices. With a greater emphasis on sustainability and efficiency, mining is likely to evolve in the coming years. Mining is here to stay as long as cryptocurrencies exist, while profitability is going to fluctuate.
Frequently Ask Questions
Q1: What does crypto mining mean?
Crypto mining verifies and adds cryptocurrency transactions to a blockchain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex puzzles, securing the network and earning cryptocurrency rewards. It’s essential for maintaining blockchain integrity and decentralization.
Q2: Is crypto mining legal?
Crypto mining legality depends on your location. It’s generally legal in North America and many other regions. However, some countries, like China, have banned it, citing energy concerns and financial stability. Always check your local regulations.
Q3: What are the best cryptocurrencies to mine in 2024?
Profitable cryptocurrencies for mining in 2024 often include Bitcoin, Ethereum Classic, Monero, and Kadena. Profitability changes based on mining difficulty, electricity costs, block rewards, and the cryptocurrency’s current market price. Consider all these before mining.
Q4: How much does it cost to mine 1 Bitcoin?
The cost to mine one Bitcoin varies significantly. Key factors are electricity rates and hardware efficiency. In 2023, estimates ranged from $12,000 to $20,000, depending on location and equipment. It is subject to considerable changes.
Q5: Is crypto mining still profitable?
Crypto mining can be profitable with efficient hardware and low electricity costs. However, increasing network difficulty, competition, regulations, and events like Bitcoin halving can significantly impact profitability. Constant evaluation is crucial for success.
Conclusion
Crypto mining is a complex but crucial aspect of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. It’s a constantly evolving field, driven by technological advancements, economic incentives, and regulatory pressures. For those considering entering the world of crypto mining, it’s essential to do thorough research, understand the risks and rewards, and stay informed about the latest developments.
Further Reading:
- What Is Cryptocurrency? – A foundational guide to understanding the broader context of crypto mining.
- What Is Bitcoin? – Understand the specifics of the most prominent cryptocurrency that utilizes mining.
- What Is Blockchain Technology? – Learn about the underlying technology that makes crypto mining necessary.
- Guide to Cryptocurrency Trading – A comprehensive view of the trading and investment aspects of cryptocurrency.
- Cryptocurrency Trading Strategies – Explore various methods to approach cryptocurrency trading.
- History of Cryptocurrency – Understanding the evolution of crypto helps appreciate the role of mining.
References & Sources
- Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (CCAF) – Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index
- Ethereum Foundation – Ethereum Merge Report
- CoinDesk – Crypto Mining Updates
- CoinTelegraph – Crypto Mining News













Pingback: What is a Crypto Stock and How Does it Work? CoinFxPro