Table of contents
- 1 Mastering the Forex Market: A Deep Dive into Major Pairs
- 1.1 I. Introduction to Major Pairs
- 1.2 II. Overview of Major Pairs
- 1.3 III. Detailed Analysis of Each Major Pair
- 1.4 IV. Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading Major Pairs
- 1.5 V. Trading Strategies for Major Pairs
- 1.6 VI. Comparison with Minor and Exotic Pairs
- 1.7 VII. Best Times to Trade Major Pairs
- 1.8 VIII. The Importance of Monitoring Economic News
- 1.9 IX. Advice for Beginners
- 1.10 X. Conclusion
- 1.11 FAQ: Major Forex Pairs
Mastering the Forex Market: A Deep Dive into Major Pairs
I. Introduction to Major Pairs
In the dynamic world of Forex, certain currency pairs stand out due to their high liquidity and trading volume. These are the major pairs. They form the backbone of the Forex market and are essential for anyone looking to trade currencies. But, what are major pairs exactly?
Major pairs are currency pairs that are most frequently traded on the Forex market, typically including the U.S. dollar (USD) paired with another major world currency. Their popularity stems from their high liquidity and relatively stable price movements compared to other currency pairs. For instance, the EUR/USD pair alone can account for approximately 28% of the total Forex market turnover, illustrating its significance. Major pairs offer tighter spreads and lower transaction costs, making them attractive to traders of all levels.
II. Overview of Major Pairs
Here is a list of the most commonly traded major pairs:
- EUR/USD (Euro vs. US Dollar)
- GBP/USD (British Pound vs. US Dollar)
- USD/JPY (US Dollar vs. Japanese Yen)
- USD/CHF (US Dollar vs. Swiss Franc)
- AUD/USD (Australian Dollar vs. US Dollar)
- NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar vs. US Dollar)
- USD/CAD (US Dollar vs. Canadian Dollar)
These pairs share several common characteristics:
- High Liquidity: They are the most actively traded pairs, making it easy to enter and exit positions at the desired price. For example, during peak trading hours, major pairs can see several thousandtrades per second, ensuring seamless execution.
- Stable Volatility: Compared to other currency pairs, major pairs tend to exhibit more stable price movements, making them easier to analyze. Although they still fluctuate, their daily average true range (ATR) is usually lower compared to minor or exotic pairs.
- Low Spreads: Due to high trading volume, these pairs typically have lower spreads, reducing transaction costs for traders, which is especially beneficial for short-term trading strategies. For example, the average spread for EUR/USD is often less than 1 pip, making it cost-effective for frequent trading.
- Strong Impact from Economic Events: Major pairs are particularly sensitive to major economic releases, such as interest rate decisions, GDP reports, and employment figures. A single unexpected announcement can lead to significant price swings.
The U.S. dollar plays a vital role in these major pairs. As the world’s reserve currency, the USD often serves as the base currency and significantly influences the value of these pairs. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the U.S. dollar accounts for approximately 60% of global foreign exchange reserves, highlighting its dominance in the Forex market.
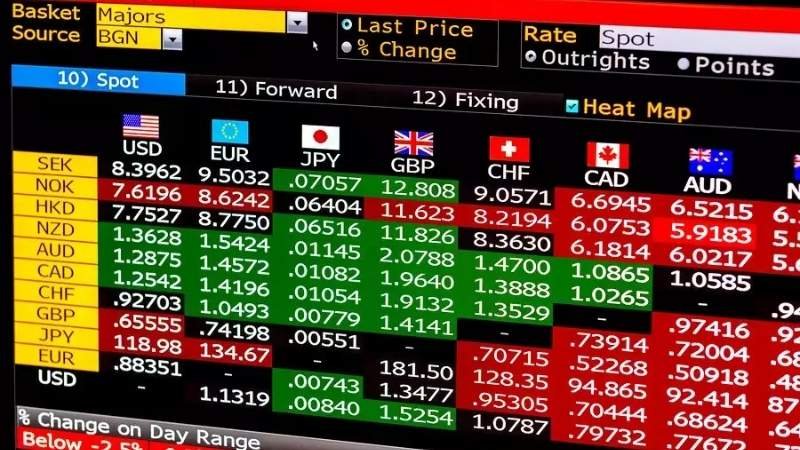
Major currency pairs displayed on a trading chart Image:
thelazytrader
III. Detailed Analysis of Each Major Pair
Let’s examine each major pair in detail:
EUR/USD (Euro vs. US Dollar)
As the most traded currency pair globally, EUR/USD offers the highest liquidity. Its price is significantly impacted by the monetary policies of the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the European Central Bank (ECB). This makes it a suitable pair for a variety of trading strategies and timeframes. For example, during the ECB rate announcement in July 2024, the EUR/USD experienced a 1.5% swing in price within a few hours. This reaction to major news events is typical and provides opportunities for well-prepared traders. Moreover, the EUR/USD pair’s movements often influence other major currency pairs, making it a bellwether for the overall market. Check out our
EUR/USD Market Watch for the latest updates.
GBP/USD (British Pound vs. US Dollar)
Known as “cable”, GBP/USD tends to be more volatile than EUR/USD. Decisions from the Bank of England (BoE) significantly impact this pair. For example, when the BoE unexpectedly raised interest rates in September 2023, the GBP/USD jumped by almost 2% in just one day. The Brexit situation also adds an extra layer of complexity to the GBP/USD pair’s movements, making it a
pair to watch carefully during political and economic news releases. According to historical volatility data, GBP/USD often exhibits a daily average true range (ATR) 10-20% higher than that of EUR/USD.
USD/JPY (US Dollar vs. Japanese Yen)
The USD/JPY pair is often considered a safe-haven currency pair. Its movements are heavily influenced by the Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) monetary policy and global risk sentiment. During times of global uncertainty, traders often flock to the Yen. For example, during periods of heightened geopolitical tension in early 2024, USD/JPY saw a decline of 2.5% as investors sought the relative safety of the Japanese yen. Additionally, changes in Japan’s bond yields often cause rapid movements in USD/JPY.
USD/CHF (US Dollar vs. Swiss Franc)
Similar to the Japanese Yen, the Swiss Franc is considered a safe-haven asset. This pair is often favored by investors looking to hedge risks. For example, during times of market volatility, the USD/CHF pair often sees increased trading volumes as investors seek the safety of the Swiss Franc. The Swiss National Bank’s (SNB) interventions in the currency market also play a significant role in this pair’s fluctuations, sometimes leading to abrupt and sizable price swings.
AUD/USD (Australian Dollar vs. US Dollar) and NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar
vs. US Dollar)
These pairs are highly correlated with commodity prices, particularly gold and agricultural products. The Australian and New Zealand economies are heavily
influenced by these commodities. For example, a surge in global gold prices will often lead to an increase in the AUD/USD pair due to Australia’s status as a major gold exporter. Similarly, changes in prices of milk products will affect NZD/USD. Data from the Australian Bureau of Statistics shows that fluctuations in commodity prices can often explain more than 60% of the
movement in AUD/USD. These pairs are popular among traders who are familiar with commodity market trends.
USD/CAD (US Dollar vs. Canadian Dollar)
The USD/CAD pair is closely tied to crude oil prices, given Canada’s position as a major oil exporter. When oil prices rise, the Canadian dollar tends to
strengthen against the U.S. dollar, impacting this pair significantly. For instance, in early 2024, when global oil prices increased by 15%, the USD/CAD pair saw a corresponding drop. According to reports from the Canadian Energy Regulator, the Canadian Dollar’s valuation is highly sensitive to crude oil price fluctuations, making it crucial for traders of this pair to stay updated on oil market trends.
IV. Advantages and Disadvantages of Trading Major Pairs
Trading major currency pairs comes with a unique set of pros and cons:
Advantages:
- High Liquidity: Easy and fast order execution due to high market activity. This allows traders to enter and exit positions with minimal slippage.
- Low Trading Costs: Small spreads, reducing transaction costs. This is especially beneficial for scalpers and day traders who make numerous trades in a short period. For example, a trader making 100 trades per day can save a substantial amount with smaller spreads.
- Stable Price Movements: Relatively predictable price behavior, suitable for various trading strategies. Though they do exhibit volatility, the patterns and reactions tend to be more consistent and easier to analyze than for exotic pairs.
Disadvantages:
- Sensitivity to Economic News: Highly reactive to significant economic announcements. Traders need to be alert and prepared for significant price movements.
- Potential for Sharp Price Swings: High volatility during news releases can lead to unexpected losses. It is essential to have proper risk management strategies in place to avoid such losses, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing.
V. Trading Strategies for Major Pairs
Several effective strategies can be used for trading major pairs:
Trend Trading
This involves identifying the direction of price movement using indicators like Moving Averages (MA) and MACD, and trading in the same direction. For example, if the 50-day moving average crosses above the 200-day moving average, it indicates an uptrend, which could suggest a buy signal. Many traders incorporate multiple time frames to validate the strength and reliability of the trend before entering a position. The use of trendlines and channels further refines the application of this strategy.
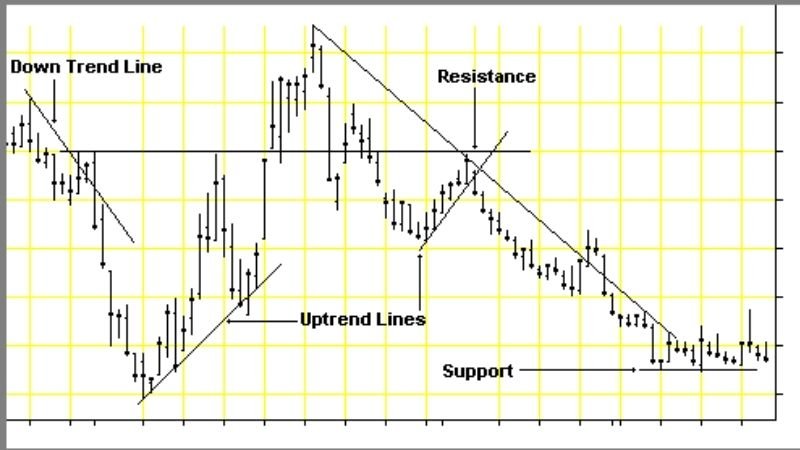
Trend Trading Strategy Image:
Reversal Trading
This involves identifying potential changes in price direction using patterns like Hammer and Shooting Star candlestick patterns. For example, a hammer
pattern appearing at the end of a downtrend could signal a potential price reversal to the upside. In conjunction with these candle stick patterns, divergence of indicators such as RSI can help confirm reversals. Reversal trading often involves more risk but can offer more significant potential rewards when identified correctly.
Scalping
This is a short-term trading strategy that utilizes small time frames (1-5 minutes), often employing technical indicators such as Bollinger Bands and RSI. Scalpers aim to capture small profits from minor price fluctuations, making multiple trades throughout the day. This strategy requires keen attention, fast decision-making, and is best suited for seasoned traders who have the time to stay glued to the screens.
Swing Trading
This longer-term strategy is based on fundamental analysis and major economic events, aimed at capturing price swings over days or weeks. Swing traders often look at economic calendars and global events to position their trades. For instance, a trader might buy EUR/USD based on positive inflation data from the EU and the expectation of a future interest rate hike from the ECB. This strategy requires a good understanding of macroeconomic factors and patience.
VI. Comparison with Minor and Exotic Pairs
Understanding the difference between major pairs and other types of currency
pairs is essential:
Major vs. Minor Pairs
- Minor pairs do not include the U.S. dollar, leading to lower liquidity and higher spreads.
- Examples include EUR/GBP and AUD/JPY, which are less traded and thus can be more volatile. For example, during normal trading hours, a minor pair such as EUR/GBP can have an average spread of 2-3 pips as compared to the average of 0.7 pips for EUR/USD, reflecting the liquidity differences.
Major vs. Exotic Pairs
- Exotic pairs consist of currencies from emerging markets, presenting higher risks but potentially higher rewards.
- Pairs like USD/TRY or USD/MXN are far less liquid, more volatile, and can be difficult to predict. According to recent volatility measures, USD/TRY can exhibit a daily average true range (ATR) 3-4 times greater than that of EUR/USD, highlighting the higher risk and reward associated with exotic pairs.
VII. Best Times to Trade Major Pairs
Market sessions significantly influence the behavior of major pairs:
Key Trading Sessions
- New York Session: Ideal for EUR/USD and GBP/USD due to high trading volume. This session sees the most activity for these pairs because it is when major US and European financial institutions are actively trading.
- Tokyo Session: Best for USD/JPY due to increased activity with Japanese Yen. This is when Japanese banks and investors are most active, leading to increased activity for this pair.
- Sydney Session: Well-suited for AUD/USD and NZD/USD, due to higher correlation with Australian and New Zealand currencies. The Sydney session’s trading volume is heavily influenced by local market participants.
Overlapping sessions, such as when the London and New York sessions overlap, often provide the highest liquidity and volatility. This period, often called the “sweet spot” for day traders, provides ample opportunities for quick profit taking, but also requires fast decision making.
VIII. The Importance of Monitoring Economic News
Major pairs are highly sensitive to economic events, including:
Key Economic Events
- Central Bank Interest Rate Decisions: Affect currency values immediately. A surprise interest rate increase can lead to a sharp spike in the corresponding currency’s value.
- Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP): A crucial employment report that impacts the USD. This report often creates a lot of volatility in major pairs, so traders need to be cautious when trading near the announcement.
- GDP and Inflation Data: Provide insights into economic performance. These data points can suggest future monetary policy changes and thus influence long term exchange rates.
Using an economic calendar can help you track upcoming events and their potential impact on your trades.

IX. Advice for Beginners
If you’re new to Forex trading, consider the following tips:
- Start with Highly Liquid Pairs: Begin with EUR/USD or GBP/USD, to familiarize yourself with trading mechanics. These pairs allow new traders to focus on learning the mechanics of trading without encountering excessive volatility or sudden price movements.
- Focus on One or Two Pairs: Concentrate on mastering one or two pairs initially, rather than spreading yourself too thin. This will provide a deeper understanding of the specific pair’s characteristics and behavior.
- Use a Demo Account: Practicing with a demo account before risking real money is crucial for developing your strategies. This allows beginners to practice strategies and get used to the trading platform without fear of losses. You can also check our reviews on MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 to find a suitable trading platform.
X. Conclusion
Major pairs form the core of the Forex market, offering opportunities for both new and experienced traders. By understanding their unique characteristics, utilizing suitable trading strategies, and staying informed about global economic events, traders can navigate the Forex market effectively. Remember to always prioritize risk management and start with a solid foundation of knowledge before trading real money. By understanding the nuances of these pairs, implementing sound risk management practices, and diligently tracking economic events, you can effectively engage in forex trading. You can also learn
How to start forex trading with our guide.
For more information, please visit: Investopedia – Major Currency Pair and BabyPips – Major Currency Pairs













Pingback: Best Forex Brokers for January 2025: A Comprehensive Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: Mastering Forex: A Guide to Currency Pairs CoinFxPro
Pingback: Mastering Forex Sentiment Analysis with Myfxbook: A Guide
Pingback: What is Netdania Charts? A Complete Guide for Forex Traders - CoinFxPro
Pingback: Understanding Pips in Forex: A Trader's Essential Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: How to Start Forex Trading: A Beginner's Guide CoinFxPro
Pingback: The Professional Trader's Guide to Forex Risk Management - CoinFxPro
Pingback: Mastering Forex Arbitrage: A Comprehensive Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: MetaTrader 5 Review: A Powerful Trading Platform CoinFxPro Forex Tools