Table of contents
- 1 The Fee Switch in Crypto: A Deep Dive into Revenue Sharing
The Fee Switch in Crypto: A Deep Dive into Revenue Sharing
Exploring the mechanics, impacts, and considerations of implementing a fee switch in DeFi projects.
In the dynamic world of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) and cryptocurrencies, the fee switch is a pivotal concept. But what is it exactly, and should projects activate it to share revenue with their token holders? This in-depth guide will explore the workings, effects, and the advantages and disadvantages of using a fee switch. Our aim is to provide a clear understanding of this crucial aspect of crypto economics.
A fee switch is a mechanism in decentralized protocols that redirects platform fees, such as trading fees or lending fees, to token holders. This process can significantly impact tokenomics and project growth by incentivizing token holding and governance participation.
Understanding the Fee Switch Mechanism
A fee switch is a mechanism within a decentralized protocol that dictates how the fees generated by the platform are distributed. Typically, DeFi protocols use these fees for:
- Operational Costs: Covering the daily expenses of managing the platform.
- Development Funds: Financing ongoing updates and improvements to the protocol.
- Liquidity Provisions: Rewarding those who contribute liquidity to the platform.
However, a fee switch enables a portion, or all, of these fees to be redirected, typically towards the holders of the platform’s native token. This can significantly alter the economic structure of the platform and the token’s role.
This mechanism is generally implemented via smart contracts, which govern the protocol. When the fee switch is activated, the rules change, and fees are redirected according to the new parameters. Activation is typically a governance decision, meaning token holders can vote on whether to switch fees.
The Activation Process of a Fee Switch
Turning on a fee switch is a complex process. It generally involves:
- Governance Vote: A proposal to activate the fee switch is put forward, and token holders vote on whether to implement it. This often involves governance tokens.
- Fee Percentage: The protocol defines the percentage of fees to be redirected to token holders. This percentage can be adjusted over time.
- Distribution Mechanism: Smart contracts manage how and when these fees are distributed, often through staking or direct payments.
- Smart Contract Implementation: The fee switch logic is programmed into the protocol’s smart contracts, ensuring transparency and verifiability. Changes can only occur via the protocol’s governance rules.
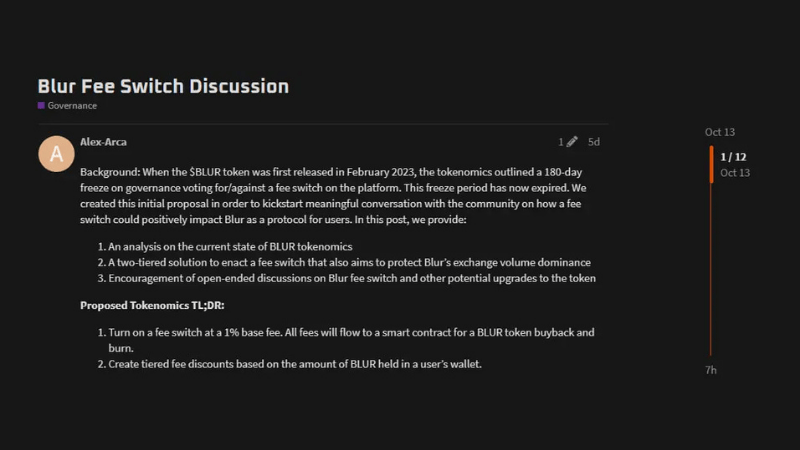
Example of a proposal focusing on fee switching. Source: Blur Foundation
The critical question remains: should projects activate the fee switch and share revenue with token holders? There are valid arguments on both sides, often dependent on the project’s objectives, development stage, and community preferences.
Arguments in Favor of Activating the Fee Switch:
- Increased Token Value: Sharing revenue directly increases token value, attracting investors and raising its price, which promotes long-term holding. This can be linked to broader cryptocurrency market trends.
- Enhanced Token Holder Incentives: Token holders become more likely to actively participate in governance and support the protocol’s growth.
- Investor Attraction: Transparent revenue-sharing models are attractive to investors, increasing platform liquidity and user base.
Arguments Against Activating the Fee Switch:
- Reduced Capital for Development: Less funding for development and protocol improvements can hinder a platform’s growth. Balancing rewards with long-term sustainability is key.
- Short-Term Thinking: Token holders may prioritize immediate gains over the protocol’s long-term health, impacting innovation and development.
- Centralization Risks: A focus on short-term financial benefits can discourage genuine users focused on long-term growth, potentially centralizing decision-making.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Various DeFi projects have experimented with fee switches, providing valuable insights:
- Uniswap: Its governance system allows community votes on activating a fee switch, underscoring its potential impact, even though not yet implemented.
- Curve Finance: Distributes a portion of fees to users locking their tokens, demonstrating the potential of revenue sharing to encourage long-term holding.
- Other Projects: Many DeFi protocols consider or have implemented similar mechanisms with varying token holder involvement and fee distribution rates.
Case Study: Project Alpha (Hypothetical)
Consider a hypothetical project, “Project Alpha,” a new lending protocol. Initially, all fees fund operations. Later, the community votes to implement a fee switch, distributing 20% of fees to token holders while the other 80% supports development and liquidity. This approach aims to balance rewarding token holders with long-term growth.
Conclusion: A Strategic Approach to Fee Sharing
The fee switch is a potent tool that can significantly impact a DeFi project’s economics and community engagement. Whether or not to activate it depends on factors including the project’s stage, priorities, and goals.
Projects must:
- Engage with the Community: Discuss the pros and cons with token holders.
- Strategize Implementation: Align the fee distribution with the project’s long-term vision.
- Consider Long-Term Impact: Balance community rewards with the project’s viability.
Ultimately, the fee switch should reflect a project’s dedication to its community and strategic objectives, and should be implemented thoughtfully and transparently. As DeFi develops, the careful use of fee switches will shape the future of these protocols by balancing growth with incentives.
Further Exploration
To delve deeper, consider the following questions:
- How does a fee switch affect tokenomics and long-term value?
- What are best practices for structuring the distribution of fees?
- What are the potential regulatory implications of activating a fee switch?
Exploring these points will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the fee switch mechanism.
Deeper Dive: Fee Switch Implications
How does the implementation of a fee switch affect tokenomics and long-term value?
The fee switch has significant effects on tokenomics and long-term value:
Tokenomics Impact:
- Enhanced Utility: The token gains a direct utility beyond governance by providing passive income.
- Demand Increase: The increased utility can lead to higher demand and potential price appreciation.
- Reduced Token Supply: Staking for fees can decrease circulating supply, leading to scarcity.
- Inflationary or Deflationary Pressure: Fee distribution can create inflationary or deflationary pressures depending on its structure. You can learn more about tokens in our articles on altcoins and Bitcoin.
Long-Term Value Implications:
- Incentive Alignment: Sharing revenue aligns project and token holder incentives, encouraging long-term commitment.
- Attracting Long-Term Investors: Sustainable, long-term returns attract strategic investors.
- Platform Stability: Long-term value is affected by how fee distribution impacts platform development and liquidity. Balance is essential.
- Risk of Short-termism: Overemphasis on immediate returns can jeopardize long-term projects and innovation.
What are the best practices for structuring the distribution of fees to token holders?
Structuring fee distribution is critical for success. Best practices include:
- Staking Mechanisms: Staking encourages users to lock up tokens, reducing circulating supply and fostering commitment. Consider exploring NFT staking for related insights.
- Lock-up Periods: Lock-up periods deter short-term speculation and increase platform stability.
- Dynamic Fee Distribution: Adjust distribution based on platform performance and market conditions.
- Governance Participation: Reward active participation in governance, creating an engaged community. Learn more about governance tokens.
- Transparency: Use transparent smart contracts and clear documentation.
- Regular Review: Adjust parameters to maintain balance and sustainability.
- Avoid Inflationary Practices: Distribute existing revenue rather than minting new tokens.
- Tiered Rewards: Offer different rewards based on lock-up time or amount staked to deepen user engagement.
What are the potential regulatory implications of activating a fee switch?
Regulatory implications can be significant, including:
- Securities Regulations: If the token is deemed a security, projects may face registration and compliance requirements.
- Tax Implications: Fee distribution can create tax obligations for both the project and token holders. For managing your crypto taxes, you might find the articles on Koinly and Cointracker to be helpful.
- KYC/AML Compliance: Projects may need to implement KYC/AML procedures to verify users and monitor transactions.
- Jurisdictional Differences: Regulations can vary, requiring projects to consider registration and user locations.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Projects must constantly adapt to evolving regulations in the crypto and DeFi space.
- Legal Advice: Seeking expert legal advice is vital for minimizing regulatory risks.
In conclusion, while the fee switch is powerful for aligning incentives and boosting token value, it’s important to proceed with an in-depth understanding of its impact on tokenomics, distribution practices, and potential regulatory consequences. If you want to trade crypto you can check out the article on guide to cryptocurrency trading, and learn how to buy crypto with the article how to buy cryptocurrency.













Pingback: How Bubblemaps Crypto Tools Revolutionize Blockchain Analytics