Table of contents
- 1 Mastering Forex: A Guide to Currency Pairs
- 1.1 What Exactly is a Currency Pair?
- 1.2 The Many Faces of Currency Pairs: Exploring the Types
- 1.3 Decoding the Language: Understanding Forex Currency Pair Symbols
- 1.4 How to Read Currency Pairs: The Art of Interpretation
- 1.5 Trading Currency Pairs: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 1.6 What Influences Currency Pairs? The Dynamics Behind Price Fluctuations
- 1.7 How Currency Pairs Work: A Deeper Look
- 1.8 How to Choose Currency Pairs: Finding the Right Fit
- 1.9 Calculating Currency Pair Price: Understanding the Math
- 1.10 Best Currency Pairs to Trade: Is There a Perfect Pair?
- 1.11 Popular Currency Pairs in Forex: The Crowd Favorites
- 1.12 Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Currency Pairs
- 1.13 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Mastering Forex: A Guide to Currency Pairs
The foreign exchange market, or Forex, is a vast, decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded around the clock. At its core, the concept of the currency pair is fundamental. Before delving into complex algorithms and advanced trading strategies, grasping what a currency pair is and how it operates is your first crucial step towards navigating this dynamic, yet occasionally volatile, financial realm. This comprehensive guide will lead you from the basic understanding of a currency pair to more advanced trading concepts.
What Exactly is a Currency Pair?
In its simplest form, a currency pair is a quotation of two different currencies, where one currency is valued against the other. Imagine it as a balancing scale: as one side rises, the other descends. In Forex trading, you are not simply buying or selling a single currency; instead, you are exchanging one currency for another. This pair is typically represented with a slash separating the two currencies, such as EUR/USD. The first currency in the pair is known as the base currency, while the second is the quote currency.
Base Currency vs. Quote Currency
The base currency serves as the foundation of the pair, representing what you are either buying or selling. On the other hand, the quote currency denotes the amount of the second currency needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, if the rate is 1.10, it means that €1 (the base currency) can be exchanged for $1.10 (the quote currency). Let’s look at a real-world example, imagine you are travelling to Europe, and you are exchanging $1100, and receiving €1000, then the exchange rate EUR/USD is 1.10
The Many Faces of Currency Pairs: Exploring the Types
There are generally three primary categories of forex currency pairs, each characterized by distinct properties, liquidity, and associated risks:
Major Currency Pairs: The Powerhouses of Forex
These pairs involve the currencies of the world’s largest economies and are the most actively traded. They are characterized by high liquidity, tight spreads, and stability, making them popular currency pairs in Forex. Typically, major currency pairs all include the U.S. dollar (USD) paired with the Euro (EUR), the British pound (GBP), the Japanese yen (JPY), the Canadian dollar (CAD), the Swiss franc (CHF), and the Australian dollar (AUD). Examples include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD. If you are new to Forex trading, starting with these major pairs can provide a more predictable trading environment due to their high liquidity.
According to the Bank for International Settlements, the EUR/USD pair is the most traded currency pair in the world, accounting for around 28% of all forex trades.
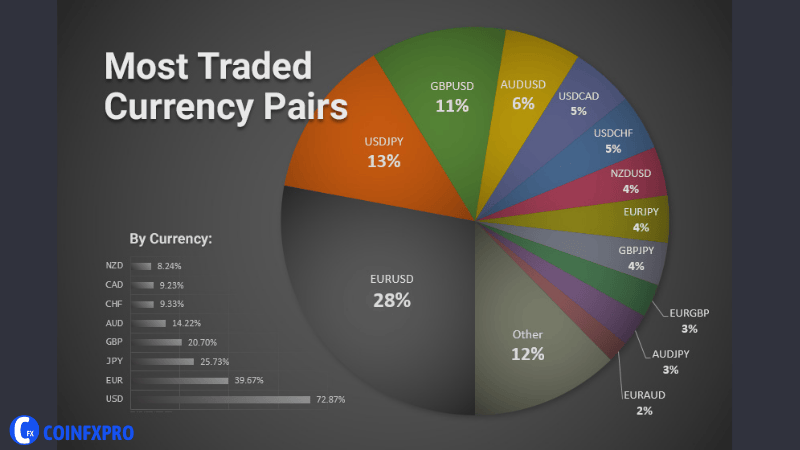
The most traded currency pairs in the world include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD Image: wp.fxssi
Minor Currency Pairs: Stepping Outside the Majors
Minor currency pairs, also known as cross-currency pairs, involve two major currencies that do not include the U.S. dollar. For instance, EUR/GBP, AUD/JPY, and GBP/CAD are considered minor pairs. These pairs tend to be less liquid than the majors, which can result in more volatile price movements. Traders often opt for minor pairs when they want to trade two specific economies without the direct influence of the dollar. These pairs can offer unique opportunities for traders who grasp their specific dynamics. For example, a trader might focus on the EUR/GBP pair if they are particularly interested in the economic relationship between the Eurozone and the United Kingdom.
Exotic Currency Pairs: The Wild Cards
Exotic currency pairs combine a major currency with a currency from a smaller or developing economy. Examples include USD/TRY (Turkish Lira), EUR/ZAR (South African Rand), and GBP/MXN (Mexican Peso). Exotic pairs can exhibit high volatility and typically have wider spreads, meaning they can be more costly to trade. They are generally favored by traders with a higher risk tolerance, those who are seeking potentially high returns, or those with expertise in a specific emerging market. For example, a trader might choose to trade USD/TRY if they have detailed knowledge of the Turkish economy and monetary policy.
Cross Currency Pairs: Understanding the Nuance
As previously mentioned, cross currency pairs are those that do not include the USD, typically referring to the minor and exotic pairs. For instance, the EUR/GBP is a cross currency pair because it does not include the USD, while the USD/MXN is not a cross currency pair because it includes the USD.
Decoding the Language: Understanding Forex Currency Pair Symbols
Each currency in a pair is represented by a three-letter abbreviation. For example, EUR stands for Euro, USD for U.S. Dollar, and JPY for Japanese Yen. These abbreviations are based on the ISO 4217 standard. It is crucial to learn these forex currency pair symbols to swiftly identify which currencies are being traded. For example, If you see “CAD/CHF” you’ll know that is the Canadian Dollar and the Swiss Franc respectively.
How to Read Currency Pairs: The Art of Interpretation
Learning how to read currency pairs is essential for any Forex trader. The price of a pair indicates how much of the quote currency is required to buy one unit of the base currency. For instance, if the price of GBP/USD is 1.2500, it means that one British pound (GBP) costs 1.25 U.S. dollars. If the price increases, it indicates that the base currency is strengthening relative to the quote currency. Conversely, if the price decreases, it means that the base currency is weakening.
Bid and Ask Price in Currency Pairs
When observing the price of a currency pair, you will encounter two numbers: the bid price and the ask price. The bid price is the price at which a broker is willing to buy a currency from you, while the ask price is the price at which a broker is willing to sell the currency to you. The difference between these two prices is the spread, which serves as a revenue source for brokers. A smaller spread is more favorable for traders. For example, if a broker has a bid price of 1.2490 and an ask price of 1.2500 for GBP/USD, then the spread would be 0.0010, or 10 pips.
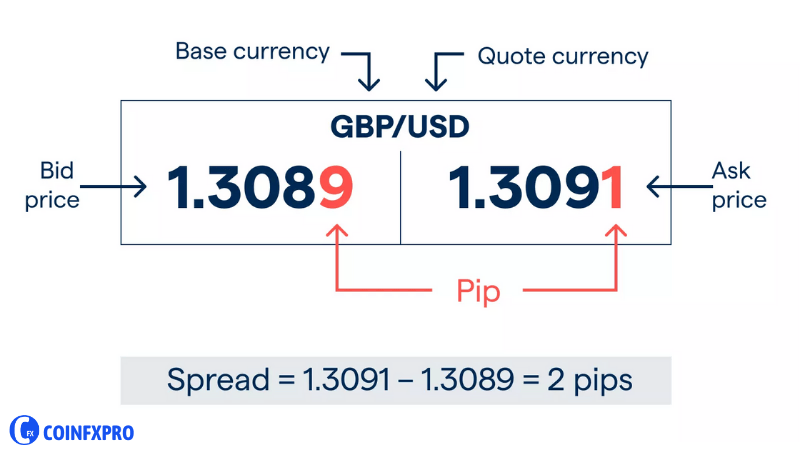
Bid and Ask Prices for GBP/USD
Trading Currency Pairs: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s explore how to trade currency pairs.
Step 1: Choose Your Broker
You will require a reliable broker to execute your trades. Consider factors such as regulation, fees, trading platform quality, and customer support. Look for brokers regulated by reputable financial authorities, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, or the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the US. Additionally, compare different brokers’ spreads, commissions, and trading tools. You can take a look at our list of the best forex brokers to help you choose.
Step 2: Choose your Currency Pair
Decide which currency pair you want to trade. Remember to research the economic and political factors that influence these currencies. For example, if you want to trade the EUR/USD, keep an eye on the economic news releases, speeches, and other political events from both Europe and the US.
Step 3: Analyze the Market
Utilize technical and fundamental analysis to make informed trading decisions. Examine historical price movements, stay informed about economic news, and be aware of major events that could induce market volatility. For example, technical traders will look for chart patterns and indicators, while fundamental traders will analyze economic reports such as the GDP or the Consumer Price Index (CPI). You may want to use tools such as TradingView, or Netdania Charts to help you analyze the markets.
Step 4: Place Your Trade
Once you have determined the anticipated direction of the currency pair, you will need to select a lot size and initiate your trade. Brokers provide various risk management tools, such as stop-loss and take-profit orders. Stop-loss orders will close a losing trade at a predetermined price, while take-profit orders will close a profitable trade at a predetermined price. For instance, if you are trading EUR/USD, you could use a stop-loss order 50 pips below your entry price, to limit your losses in case the price does not move in your favor.
Exness trading platform
Step 5: Monitor your Trade
It is crucial to actively monitor your trade and be ready to adapt your strategies if necessary. Keep an eye on economic news releases and price movements. Depending on your trading style, you may want to check your trades every 15 minutes, or maybe a couple of times a day. It will depend on your own personal preferences.
What Influences Currency Pairs? The Dynamics Behind Price Fluctuations
Understanding the factors that affect the price of currency pairs is vital for anyone engaging in Forex trading. Various factors can influence currency values, including economic indicators, political events, and market sentiment.
Economic Factors
Interest rates, inflation rates, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), and employment data can all significantly impact currency values. Countries with higher interest rates often attract investors looking for better returns, which can lead to an increase in the value of their currency. For example, if a country suddenly increases their interest rates, then their currency is likely to appreciate in value against other countries.
Political Factors
Political instability, government policies, and trade agreements can significantly affect the perception of a country’s currency. Geopolitical tensions can also lead to heightened volatility in currency markets. For example, if a country is facing a political crisis, it will cause investors to have less faith in the currency, and so they would sell the currency, causing it to depreciate in value.
Market Sentiment
Market sentiment reflects traders’ overall outlook toward a currency. If the market is optimistic about a specific economy, traders are more likely to purchase that currency, potentially causing its price to rise. Conversely, if market sentiment is negative towards a currency, then traders will sell it, causing the currency to depreciate. For example, positive sentiment towards the US economy may cause traders to buy the USD, which might cause USD/CAD to decrease. You may want to use tools such as Myfxbook to help you understand the market sentiment.
How Currency Pairs Work: A Deeper Look
How currency pairs work may seem complicated at first, but the core idea is simple: you are betting on the relative value of one currency against another. For instance, you might buy EUR/USD if you believe the Euro will strengthen against the dollar. If you are correct, you can sell the EUR/USD at a higher price to realize a profit. If you are wrong, and the Euro weakens, you will incur a loss. Understanding this relationship is crucial to be able to understand currency pairs in Forex.
How to Choose Currency Pairs: Finding the Right Fit
Choosing the most appropriate currency pair to trade depends on your trading strategy, risk tolerance, and understanding of various markets.
Considering Volatility
Certain pairs, such as GBP/JPY, tend to be more volatile than others, such as EUR/USD. This volatility can provide more opportunity, but also carries a higher degree of risk. For example, traders who are more risk averse may prefer to trade EUR/USD, while traders who are more risk tolerant may prefer trading GBP/JPY.
Analyzing Liquidity
Pairs with greater liquidity usually have tighter spreads, making them less expensive to trade. Currency pairs and liquidity are very important considerations when trading. High liquidity allows for easier order execution and reduced slippage. EUR/USD is an example of a currency pair with high liquidity. In contrast, USD/TRY has lower liquidity, which means that spreads will be larger.
Personal Preference and Knowledge
Consider pairs that you understand or have a particular interest in. Being aware of the geopolitical and economic factors that influence these pairs can provide you with a competitive advantage. For example, if you live in the UK, you may know more about the UK economy, and so you may decide to trade GBP/USD.
Calculating Currency Pair Price: Understanding the Math
Although trading platforms handle the calculations for you, understanding how to calculate currency pair price can be beneficial. The price is determined by supply and demand, as well as all of the factors we have previously discussed. Forex rates are also calculated and presented by different financial institutions, so the final price is typically an average of all these prices.
Best Currency Pairs to Trade: Is There a Perfect Pair?
The “best” pair depends on individual factors, but some of the best currency pairs to trade for beginners are the majors because they are more stable, have higher liquidity, and tighter spreads. Generally, focusing on a select number of pairs that you understand well is more effective than trying to trade too many at once. Experts often recommend beginners should only focus on 1 or 2 major pairs, and start off with a demo account first.
Popular Currency Pairs in Forex: The Crowd Favorites
Some of the most popular currency pairs in Forex include EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and AUD/USD. These pairs are popular due to their high liquidity, relatively low spreads, and because they represent the economies of some of the world’s most prominent powers. They also tend to be more stable in terms of price movement, which is more appealing to beginners in forex.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Currency Pairs
Grasping the concept of currency pairs in Forex trading is the cornerstone of successful Forex trading. It is not simply about memorizing symbols, but rather understanding the underlying economic forces, market dynamics, and strategic nuances that influence currency fluctuations. By delving into the nature of currency pairs, how to read currency pairs, the different types of currency pairs, and all of the influences behind them, you will equip yourself with the knowledge required to navigate the Forex market with more confidence. Remember, knowledge and consistent practice are key, so continue learning and refining your approach. If you’re just starting out with forex trading, we recommend you check out our guide on how to start forex trading. Additionally, you should look at the what is the forex market page, and also what is a trading strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a currency pair in Forex?
A currency pair is a quotation of two different currencies, with the value of one currency being quoted against the other. For example, EUR/USD shows the Euro’s value against the US Dollar. It reflects their relative value based on market forces.
What are the types of Forex currency pairs?
Forex pairs are categorized into majors (e.g., EUR/USD), minors (cross-currency pairs without USD), and exotics (major currency paired with emerging market currency). Majors have the highest liquidity; exotics the lowest and most volatile.
How do I read a currency pair?
The first currency is the base, and the second is the quote. The price indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency. Example: EUR/USD at 1.10 means 1 Euro costs 1.10 US Dollars.
What influences the price of currency pairs?
Key factors include interest rates, inflation, economic indicators (like GDP and employment), political stability, and overall market sentiment. Central bank actions and global news significantly impact currency valuations, causing price fluctuations and volatility.
What are the best currency pairs to trade?
High-liquidity major pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY) are commonly recommended. They offer tighter spreads and lower volatility, making them suitable for various trading styles including beginner-friendly environments. Consider your risk tolerance.













Pingback: Decoding EUR/USD: A Comprehensive Guide with MarketWatch
Pingback: How to Start Forex Trading: A Beginner's Guide CoinFxPro
Pingback: Decoding the Forex Market: A Comprehensive Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: What is Binance App? A Comprehensive Guide CoinFxPro Trading Tools
Pingback: Mastering Forex Arbitrage: A Comprehensive Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: What is Netdania Charts? A Complete Guide for Forex Traders - CoinFxPro
Pingback: Mastering the Forex Market: A Deep Dive into Major Pairs - CoinFxPro
Pingback: All Forex No Deposit Bonus: Guide to Risk-Free Trading CoinFxPro
Pingback: Understanding Pips in Forex: A Trader's Essential Guide - CoinFxPro
Pingback: Uncle Ted Forex: Exploring Proven Trading Strategies CoinFxPro Learn Forex
Pingback: Navigating the World of Forex Brokers: A Comprehensive Guide - CoinFxPro